Figure 3. ND‐011992 has a low spontaneous resistance mutation frequency and is active against drug‐resistant M. tuberculosis clinical isolates.
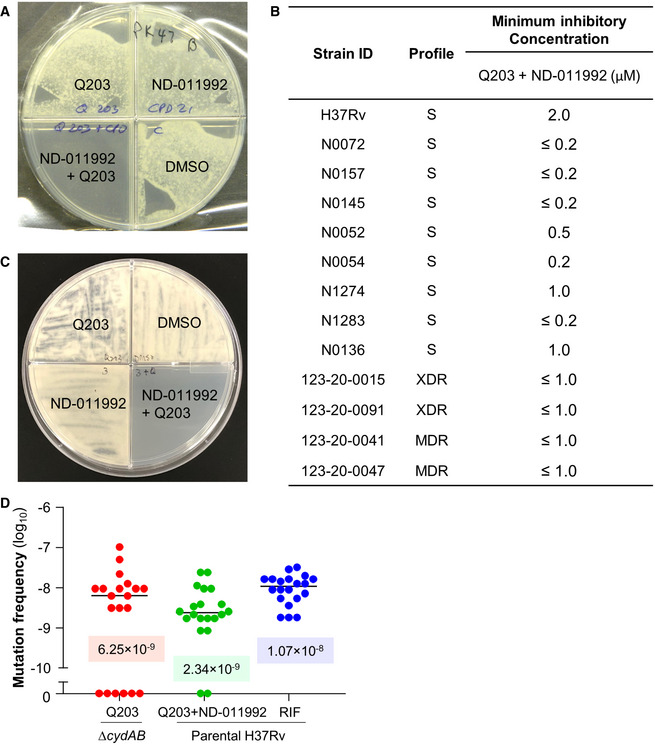
- Combined potency of ND‐011992 + Q203 against the drug‐resistant clinical isolate M. tuberculosis 123‐20‐0047.
- Potency of the combination ND‐011992 + Q203 against various clinical isolates in an agar plate MIC assay. A dose range of ND‐011992 was tested against the clinical isolates in the presence of Q203. Q203 was used at 100 nM against the strains H37Rv, N1274, N1283, 123‐20‐0015, 123‐20‐0091, 123‐20‐0041, 123‐20‐0047, and at 20 nM against the stains N0072, N0157, N0145, N0052, and N0136. “S” indicates pan‐susceptibility to anti‐TB drugs; “MDR”: multi‐drug resistant; “XDR”: extensively drug‐resistant.
- Growth inhibition assay in M. bovis BCG. 106 bacteria were plated onto 7H10 agar supplemented with DMSO, 25 nM Q203, 3 µM ND‐011992, or 25 nM Q203 + 3 µM ND‐011992.
- Fluctuation analysis in M. tuberculosis H37Rv. M. tuberculosis ΔcydAB was plated on 7H10 containing 100 nM Q203 (red). Parental H37Rv was plated on 7H10 with 100 nM Q203 and 6 µM ND‐011992 or 2 µg/ml rifampicin (blue). The corresponding values of the median frequency of resistance are indicated in the graph.
