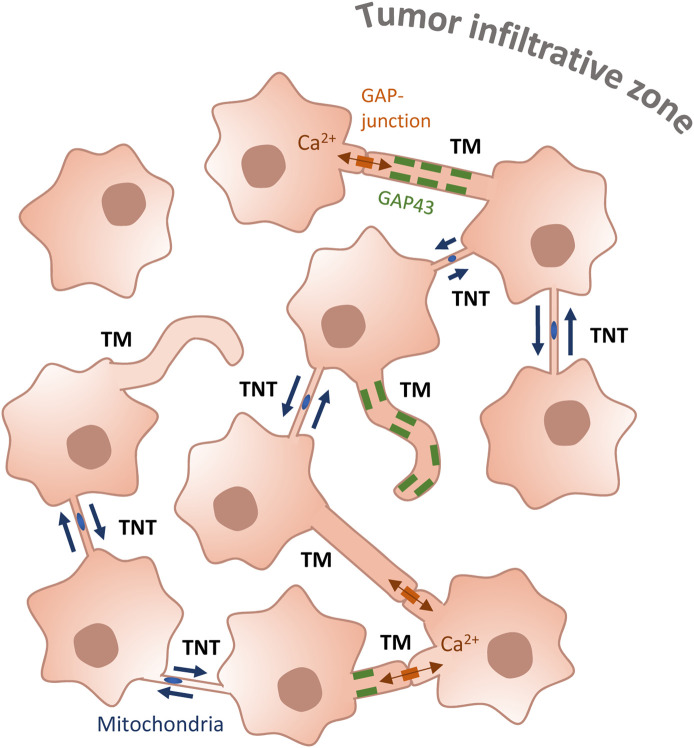
Figure 7. GSLC network.
GSLCs interconnect through different types of cellular extensions. TMs are thick (>1 µm) protrusions that can either contact other cells through GAP-junctions, allowing the propagation of calcium flux, or be individual finger-like extensions not connecting remote cells. They can be positive for GAP43 (rectangles along the membranes of TM), neuronal Growth-Associated Protein. GSLCs also interconnect through TNTs, thinner (<1 µm), open-ended connections which allow transfer of cellular cargos, such as mitochondria (ovals in TNTs).