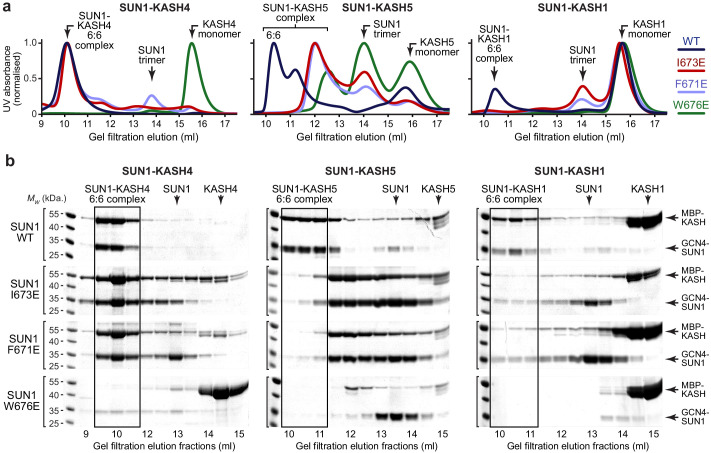
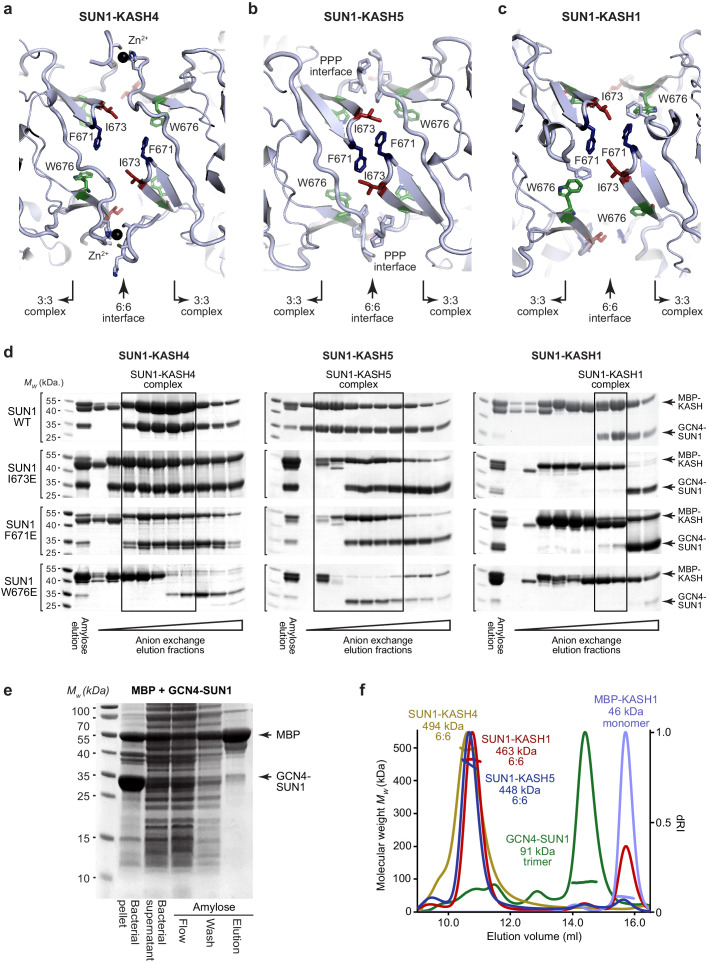
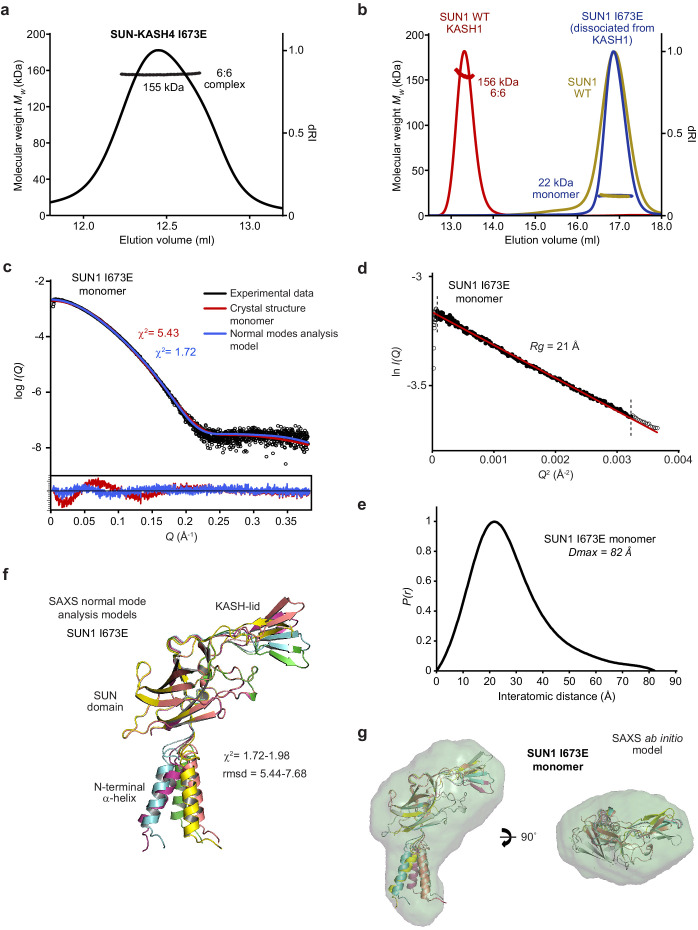
Figure 4. SUN1 KASH-lid residues involved in 6:6 assembly are essential for KASH1-binding.
(a,b) Gel filtration analysis. GCN4-SUN1 and MBP-KASH proteins were co-expressed and purified by amylose affinity (utilising non-specific binding by SUN1 for non-interacting mutants) and ion exchange (Figure 4—figure supplement 1d), and all fractions containing SUN-KASH complexes and dissociated proteins were concentrated and loaded onto an analytical gel filtration column. The elution profiles were validating by SEC-MALS in which wild-type fusion complexes and dissociated GCN4-SUN1 and MBP-KASH1 proteins were found to be 6:6 complexes, trimers and monomers, respectively (Figure 4—figure supplement 1f). (a) Gel filtration chromatograms (UV absorbance at 280 nm) across elution profiles for SUN1 wild-type (WT; dark blue), I673E (red), F671E (light blue), and W676E (green), with KASH4 (left), KASH5 (middle), and KASH1 (right), and (b) SDS-PAGE of their corresponding elution fractions. Representative of three replicates using different protein preparations. Source data are provided in Figure 4—source data 1.