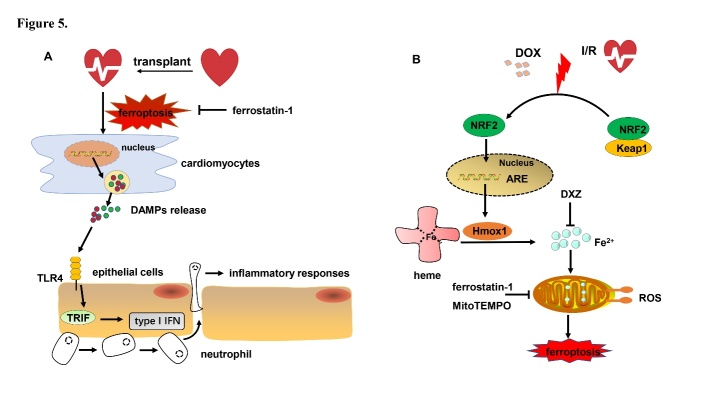
Figure 5.
The role of ferroptosis in CVDs. (A) Heart transplantation leads to cardiomyocytes ferroptosis and the release of multiple DAMPs. These DAMPs trigger TLR4/TRIF/Type I IFN signaling in endothelial cells, which recruits neutrophils and results in inflammatory responses. (B) Cardiomyocyte ferroptosis responses to DOX and IRI exposure. Heart exposed to DOX and transient IRI causes Hmox1 upregulation modulated by the Keap1/NRF2 signal pathway. Hmox1 catalyzes heme degradation and causes iron overload, which results in lipid peroxidation and tissue damage. DAMPs: damage associated molecular patterns; TLR4: toll like receptor 4; TRIF: toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 1; DOX: doxorubicin; I/R: ischemia and reperfusion; Keap1: Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; IFN: interferon; NRF2: nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; DXZ: dexrazoxane; ROS: reactive oxygen species; ARE: antioxidant response element.