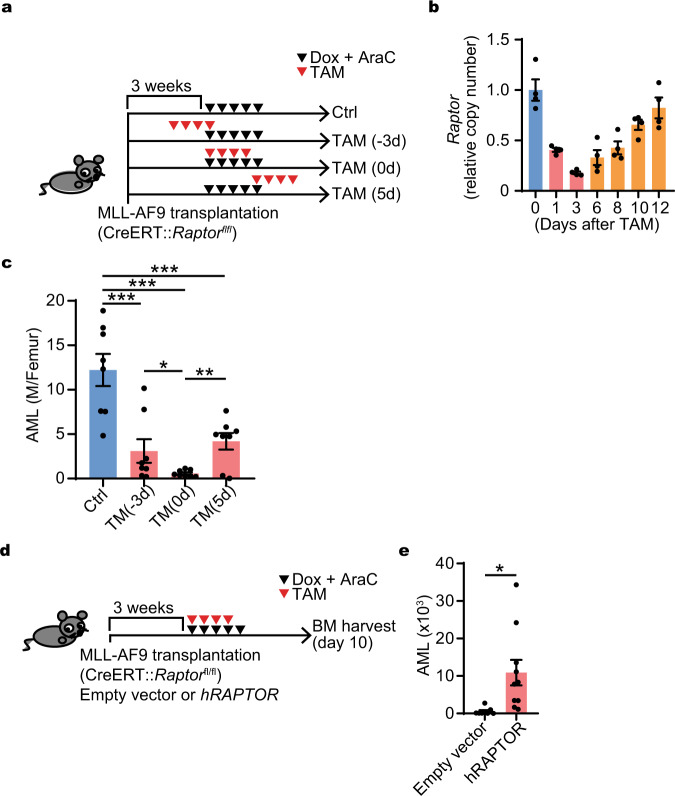
Fig. 5. Timed inhibition of mTORC1 with chemotherapy improved AML burden.
a Experimental design of mTORC1 timed inhibition in combination with chemotherapy. MLL-AF9 cells (GPF+, CreERT::Rptorfl/fl) were transplanted 3 weeks before the start of chemotherapy (Dox + Ara-C), which was started day 0 with (TAM) or without (Ctrl) Tamoxifen (TAM for 4 days started at day −3, 0, or 5). b Kinetics of Raptor deletion efficiency days before (day 0) and after starting the 4 days of Tamoxifen (TAM) treatment (day 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, and 12) (n = 4). c AML burden with or without inducible Raptor deletion in combination with chemotherapy (n = 8). d Experimental design of retroviral transduction of hRAPTOR for rescue of Raptor deletion: The number of AML cells was evaluated at day 10 after initiation of chemotherapy (Dox + AraC). e AML burden with or without rescue: AML cell number per femur was evaluated. Empty vector and hRAPTOR were transfected (empty vector: n = 8, hRAPTOR n = 10). b–c, e Representative data from two independent experiments were shown. Mean ± SEM was shown in bar pot (each dot represents each sample). Statistical analysis was performed by using two-way t-test (e) and paired t-test (b, c) (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).