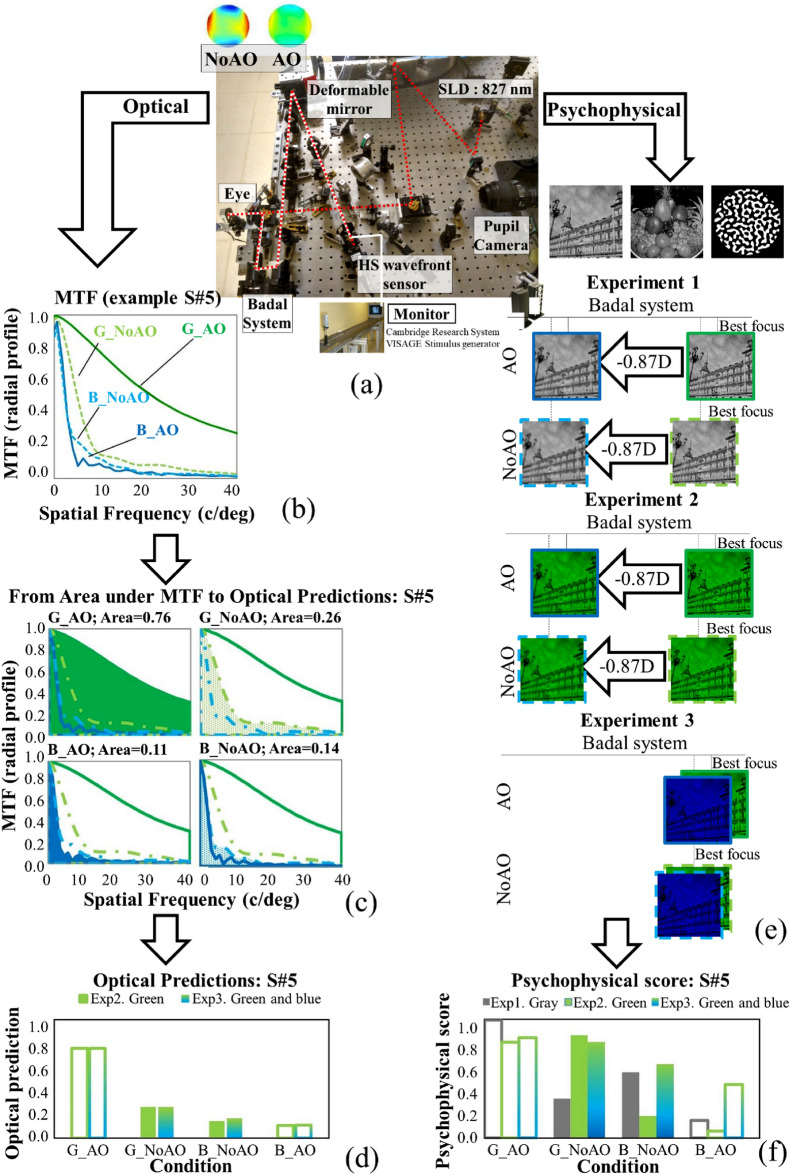
Figure 1.
Methods overview. Example of Optical predictions (left) and Psychophysical scores (right) for one subject (S#5) from experimental measurements in the Adaptive Optics system (with natural and AO-corrected aberrations, depicted in (a)). The optical modulation transfer functions (MTFs) were obtained from the measured wave aberrations at best focus for Green (NoAO, dotted line and AO, solid line) and for a defocus corresponding to the chromatic difference of focus for Blue (b). Optical quality predictions are estimated computing the normalized area under the MTF (0–40 c/deg range) (c,d). The patients then scores the perceived quality of natural images (city scene, fruit platter and binary noise) of gray-scale images (in focus, and defocus by − 0.87 D), green images (in focus, and defocus by − 0.87 D), and green and blue images (in the best focus of green), both with natural aberrations (NoAO) and aberration correction (AO), illustrated in (e). Psychophysical scores are obtained from the perceptual judgment of natural images (0–5) as seen through the Adaptive Optics system in 4 conditions (G_AO, G_NoAO, B_NoAO) and normalized to 1 (f). Note that G_AO and G_NoAO means best focus of gray-scale images in Exp 1 and best focus for green in Experiment 2 and 3, for AO and NoAO conditions, respectively, and B_AO and B_NoAO means − 0.87 D from the best focus of gray-scale images and green images, for Experiment 1 and 2, respectively, and best focus of green (with blue stimuli) in Experiment 3.