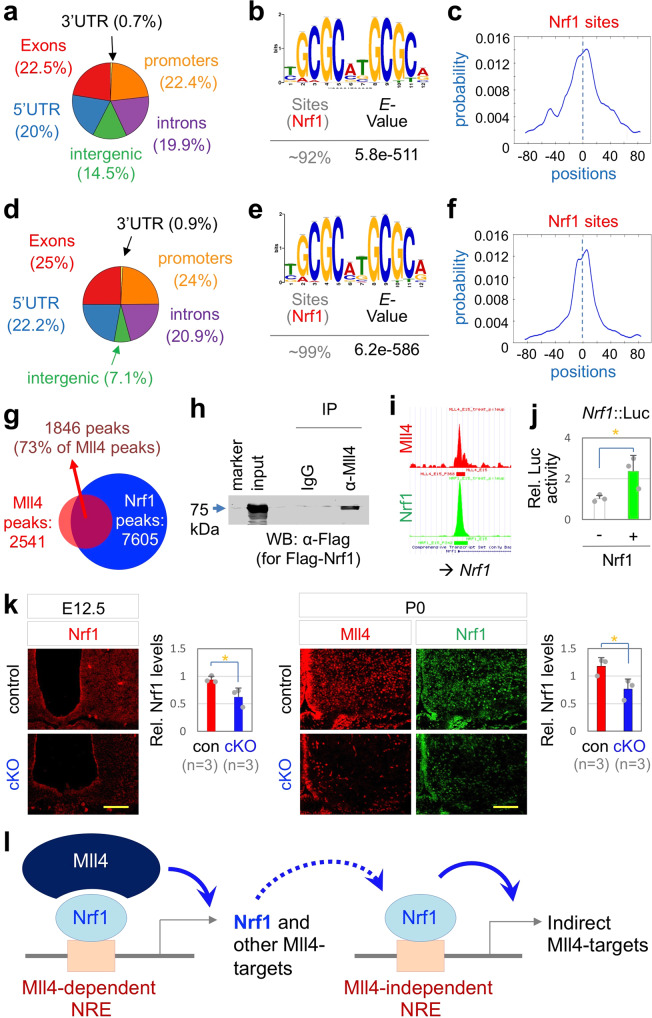
Fig. 4. Nrf1 is a major partner transcription factor of Mll4 in developing hypothalamus.
a–f Location of ChIP-seq peaks in E15 hypothalamus shown for Mll4 ChIP-seq (a) and Nrf1 Chip-seq (d), Nrf1-binding motif found in de novo motif analysis of the top 300 Mll4 peaks (b) and Nrf1 peaks (e), and the enrichment of the Nrf1-binding motif in the center of the peaks for Mll4 (c) and Nrf1 (f). g 73% of Mll4 ChIP-seq peaks overlap with Nrf1 ChIP-seq peaks, suggesting recruitment of Mll4 to a majority of its targets via Nrf1. h CoIP of Mll4 and Flag-Nrf1 in HEK293 cells. Similar results were obtained from at least three independent experiments. i An identical locus of the promoter region of Nrf1 gene is associated with Mll4 and Nrf1 ChIP-seq peaks. j A luciferase reporter construct directed by the genomic region containing the Nrf1-associated Nrf1/Mll4-binding locus (i) is activated by ectopic expression of Nrf1 in HEK293 cells. Three independent experiments (each experiment done in duplicate) were analyzed together. k Nrf1 expression is reduced in Mll4-cKO at both E12.5 and P0 relative to their littermate controls (n = 3, each genotype). Scale bars, 100 µm. Statistical differences were determined by two-sided Student’s t-test (j, k); *p < 0.05. Column bars represent mean, error bars indicate the SEM (j) and SD (k). l A model for direct and indirect target genes of Mll4 in the developing hypothalamus. The Nrf1 gene is a direct target of Mll4:Nrf1, and therefore genes regulated by Nrf1 alone can be classified as indirect target genes of Mll4.