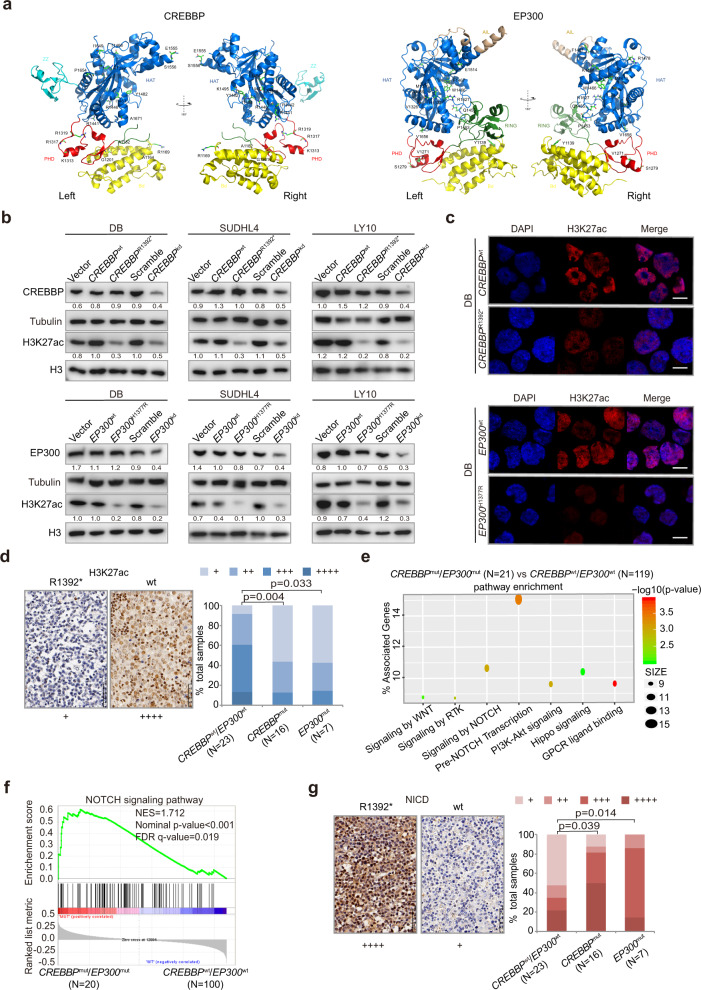
Fig. 3.
CREBBP/EP300 mutations inhibited H3K27 acetylation and activated the NOTCH signaling pathway. a Structure prediction of the complex of CREBBP and EP300 mutations. b Protein expression of CREBBP and H3K27ac detected in vector, CREBBPwt, CREBBPR1392*, scramble, CREBBPkd, protein expression of EP300 and H3K27ac in vector, EP300wt, EP300H1377R, scramble, EP300kd of DB, SUDHL4, and LY10 cells by western blot. Tubulin and H3 were used as loading controls. The CREBBP/tubulin, EP300/tubulin, and H3K27ac/H3 ratio are shown. c Immunofluorescence assay of H3K27ac in CREBBPR1392* and EP300H1377R DB cells. d Immunohistochemical study of H3K27ac in tumor samples of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients with and without CREBBP/EP300 mutations. e Pathway enrichment analysis in DLBCL patients with or without CREBBP/EP300 mutations according to the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and Reactome databases. f Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) enriched differentially expressed genes in NOTCH signaling pathway with or without CREBBP/EP300 mutations. Enrichment scores were listed with P value. NES normalized enrichment score, FDR false discovery rate. g Immunohistochemical study of NICD (intracellular portions of NOTCH1) in tumor samples of DLBCL patients with or without CREBBP/EP300 mutations