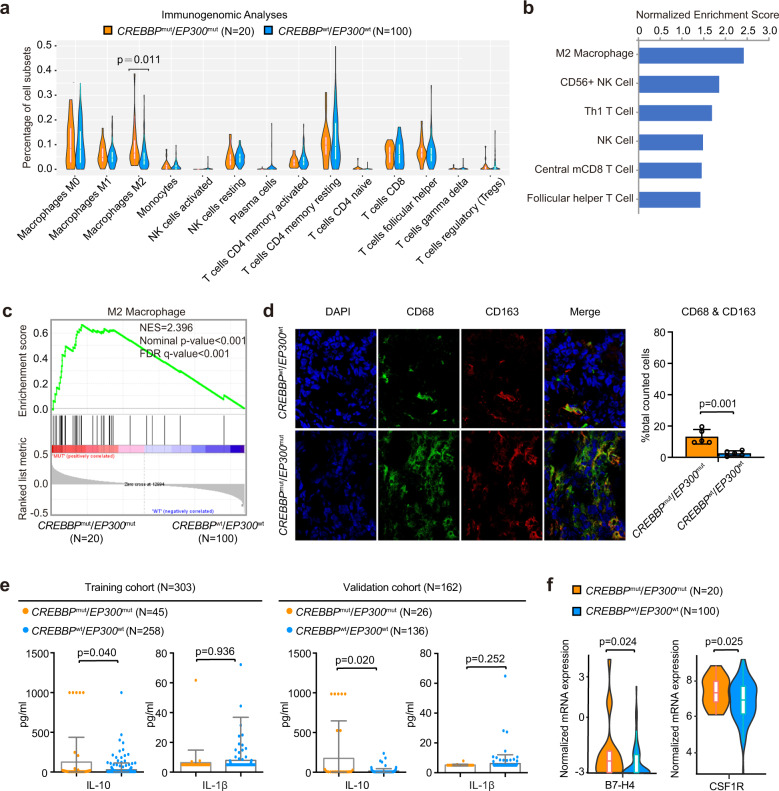
Fig. 5.
CREBBP/EP300 mutations contributed to macrophage activation and polarization. a Distribution of immune subpopulations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients with or without CREBBP/EP300 mutations analyzed by computational deconvolution of transcriptomics data using Cibersort. b Prediction of immune subpopulations normalized enrichment scores for DLBCL patients with CREBBP/EP300 mutations using GSEA. Immune cells with P < 0.05 are listed. c GSEA showing association of M2 macrophage gene signatures with CREBBP/EP300 mutations in DLBCL patients. NES normalized enrichment score, FDR false discovery rate. d Confocal analysis of CD68 and CD163 in DLBCL patients with or without CREBBP/EP300 mutations. The cells were counted from five randomly selected visions and subjected for statistical analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. e Chemiluminescence immunoassay of IL-10 and IL-1β in the training and validation cohorts of DLBCL patients according to CREBBP/EP300 mutations. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. f Normalized mRNA expression of immune inhibitors (B7-H4 and CSFR1) in DLBCL patients with or without CREBBP/EP300 mutations as revealed by RNA sequencing data