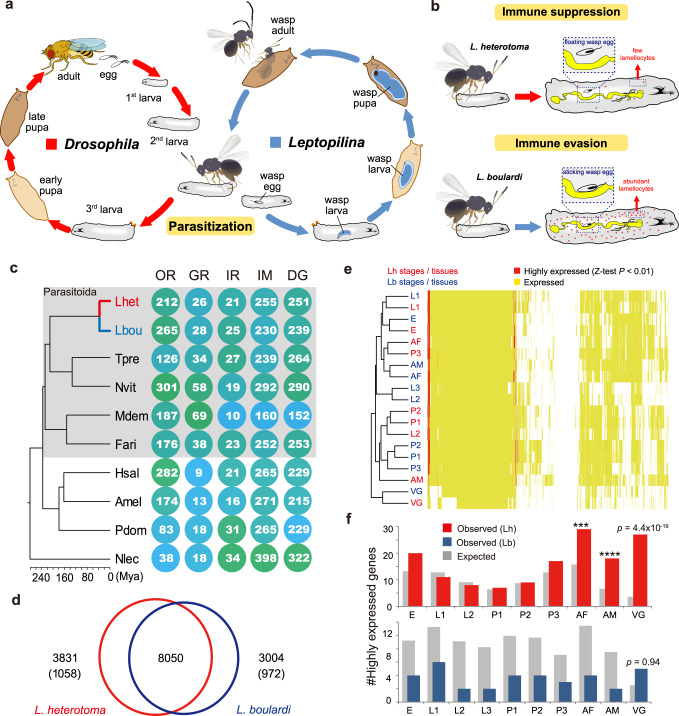
Fig. 1. Comparison between Lh and Lb in ecological and genomic contexts.
a The life cycle of Leptopilina (parasitoid) and Drosophila (host). Both L. heterotoma (Lh) and L. boulardi (Lb) are known as larval–pupal parasitoids that deposit their eggs into second instar Drosophila larvae; the growing adults emerge from the host pupa shell approximately 3 weeks later. b Different strategies by which Lh and Lb avoid host immune responses. c Phylogenetic relationships and estimated divergence times among hymenopteran species based on 2401 single-copy orthologous genes. The calibration time was based on a previous study17. Right: gene family evolution of representative systems with important roles in parasitoid biology. Circles with a green background indicate gene family expansion, while those with a blue background indicate contraction. OR olfactory receptors, GR gustatory receptors, IR ionotropic receptors, IM immune systems, DG digestive systems, Tpre T. pretiosum, Nvit N. vitripennis, Mdem M. demolitor, Fari F. arisanus, Hsal H. saltator, Amel A. mellifera, Pdom P. dominula, Nlec N. lecontei. d Gene repertoire comparison between Lh and Lb. Numbers in brackets indicate species-specific genes. e Heatmap of expression profiles across developmental stages and in venom glands. Each column indicates an orthologous gene pair between Lh and Lb; yellow indicates expression in the corresponding stage (tissue), while red indicates high expression. E eggs, L1 days 1–3 larvae, L2 days 4–9 larvae for Lh while days 4–6 larvae for Lb, L3, days 7–9 larvae for Lb, P1 days 1–3 pupae, P2 days 4–7 pupae, P3 days 8–10 pupae, AF female adults, AM male adults, VG venom glands. f Enrichment analysis of highly expressed species-specific genes. Hypergeometric test (higher tail): Bonferroni-adjusted ***P < 0.005 (AF, P = 0.0043; AM, P = 0.0003), ****P < 0.001. Source data are provided as a Source data file.