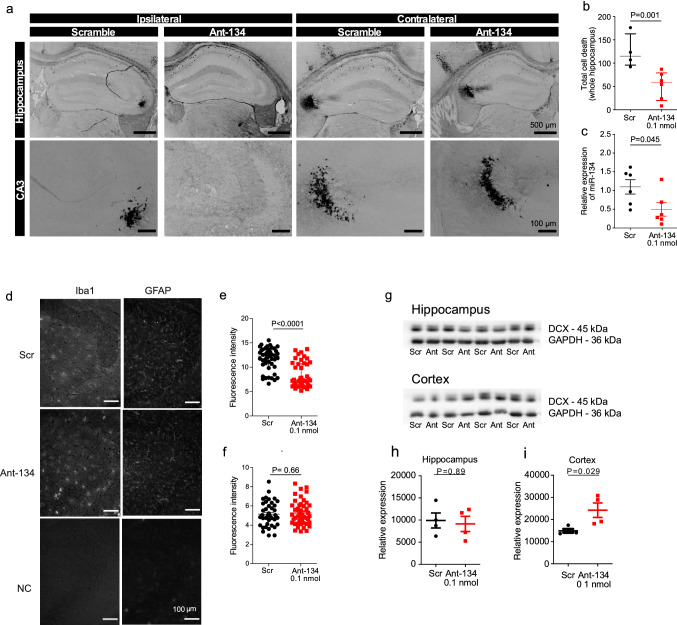
Figure 6.
Ant-134 has protective effects in the hippocampus and de-represses cortical DCX. (a) Representative FJB-stained images show neuronal death in the hippocampus 24 h after SE ipsi- and contralateral to pre-treatment with 0.1 nmol Ant-134 or scramble control (Scr). (b) The number of FJB-stained cells was reduced in mice pre-treated with Ant-134 (N = 6) compared with scramble control (N = 4). (c) Partial knockdown of miR-134 levels (54.8%) was retained 24 h after SE in the hippocampus of mice that were pre-treated with 0.1 nmol Ant-134 (N = 6) or Scr (N = 6). (d) Representative immunohistochemistry staining with Iba1 and GFAP in the CA3 of the hippocampus after SE. (e) The number of activated microglia was decreased in mice pre-treated with Ant-134 (N = 3) compared with scramble control (N = 3). (f) There was no difference in the number of astrocytes in mice pre-treated with Ant-134 (N = 3) and scrambled control (N = 3). (g) Western blot showing DCX expression in hippocampus and cortex at 24 h after KA-induced seizures of mice pre-treated with Scr/Ant-134 (0.1 nmol). Full-length blot can be found in Supplementary Fig. S3a. (h) Densitometry analysis of DCX in the hippocampus. GAPDH was used as the loading control, (N = 4/group). (i) Densitometry of DCX in the cortex. GAPDH was used as the loading control (N = 4/group).