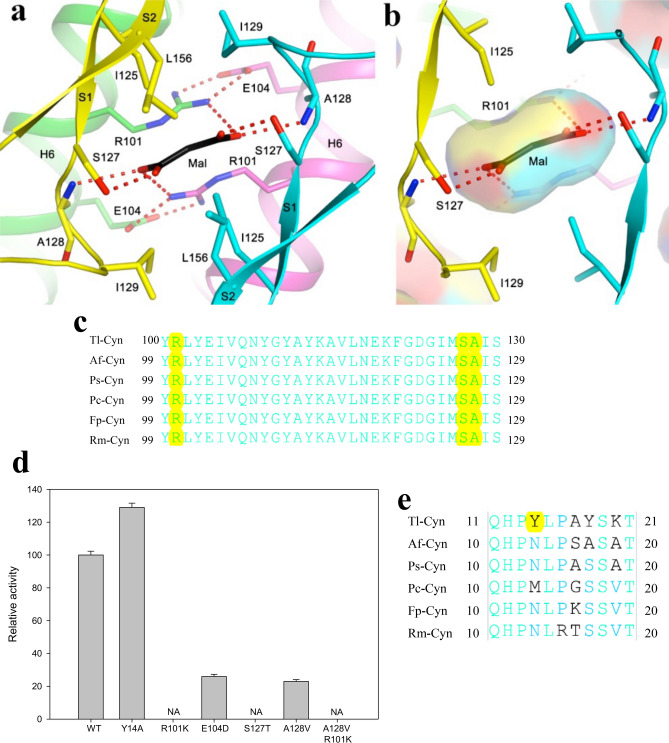
Figure 3.
Structural insights into the catalytic mechanism of Tl-Cyn. (a) Schematic drawing of the detailed interactions between Tl-Cyn and the malonate molecule bound in the active site (sticks model and labeled Mal). Hydrogen-bonding interactions with the malonate are indicated with dashed lines (red). (b) Close-up view to that in (a), and the internal cavity for malonate is shown with semi-transparent surface. (c) Conserved sequence near the active site region of the C-terminal domain in fungal cyanases are shown in cyan. Residues that interact with Mal are shown with yellow background. Tl: Thermomyces lanuginosus, Af: Aspergillus flavus, Ps: Penicillium subrubescens, Pc: Phaeomoniella chlamydospora, Fp: Fonsecaea pedrosoi, Rm: Rhinocladiella mackenziei. (d) Catalytic activities of wild-type (WT) and mutant Tl-Cyn. The cyanate concentration is at 2 mM. The error bars represent the standard deviation from three independent measurements. NA, no activity observed under the condition tested. (e) Sequence alignment for the N-terminal domain of the fungal cyanases. Conserved residues are in cyan and a unique Y14 residue in Tl-Cyn is shown with yellow background.