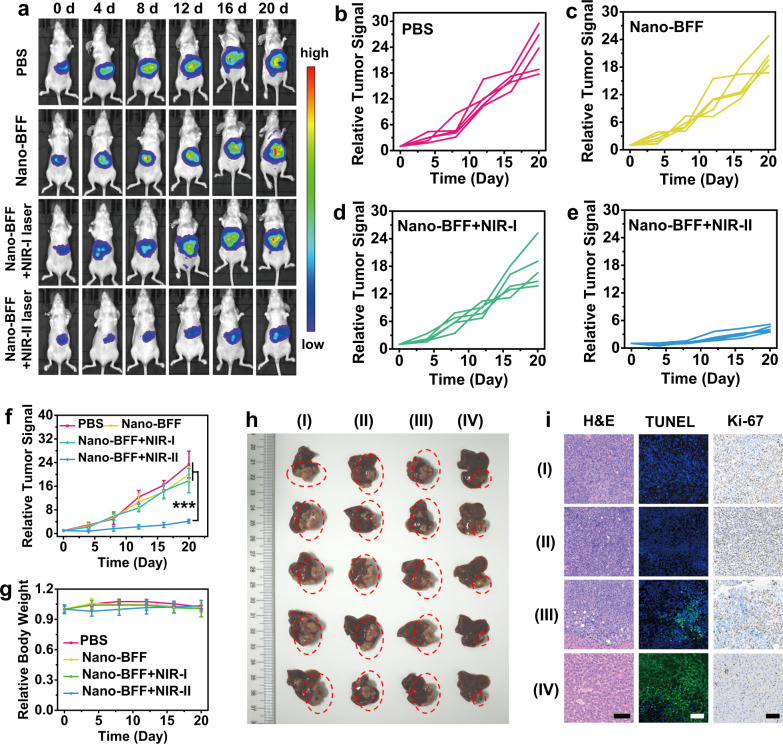
Fig. 7. In vivo antitumor performance of Nano-BFF toward orthotopic HCC.
a Bioluminescence images of the mice treated with PBS, Nano-BFF, Nano-BFF + NIR-I laser, and Nano-BFF + NIR-II laser on days 0, 4, 8, 12, 16, and 20, respectively (n = 5 biologically independent samples). b–e Relative orthotopic liver tumor luminescence levels of mice after various treatments, including b PBS, c Nano-BFF, d Nano-BFF + NIR-I laser, and e Nano-BFF + NIR-II laser. f Relative orthotopic liver tumor luminescence levels of the mice, and g body weight variations of the mice in various treatment groups within 20 days (n = 5 biologically independent samples). Scale bars: 100 μm. Data are presented as mean values ± SD. p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, analyzed by Student’s two-sided test. h Photographs of liver tissues in each treatment group, where the orthotopic tumor tissues were highlighted with red dotted circles. i Histological images of the orthotopic liver tumor tissues using H&E, TUNEL, and Ki-67 staining assays (I: PBS; II: Nano-BFF; III: Nano-BFF + NIR-I laser; IV: Nano-BFF + NIR-II laser). A representative image of three biological replicates from each group is shown.