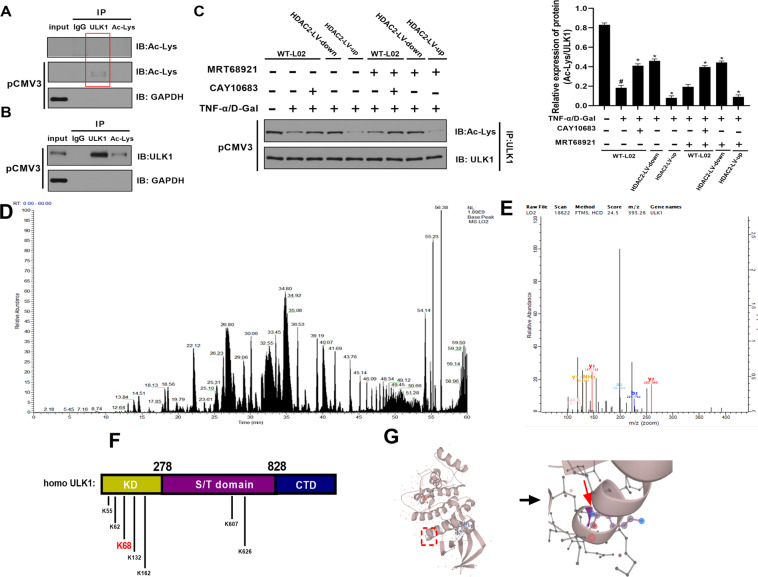
Fig. 3. HDAC2 deacetylating ULK1 by lysine K68 site.
A Total protein in L02 cells was directly extract, then performed with IP for ULK1 protein and Ac-Lys protein. The IB experiment with Ac-Lys protein was then perform. It could be found that ULK1 and Ac-Lys were not bound. However, after L02 cell was transfected with ULK1 overexpression pCMV3 vector, the amounts of Ac-Lys combined with ULK1was obviously increased. B After L02 cell was transfected with ULK1 overexpression pCMV3 vector, the amounts of ULK1 combined with Ac-Lys or ULK1 was obviously observed. C After interfering with L02 cells in different ways, the protein expression of ULK1 should have been different. However, in order to control the variables, we adjusted the expression of ULK1 by homogenizing the gray value of ULK1 in the western blot gels, and observed the effect of HDAC2 on the acetylated lysine on ULK1 protein under the same expression of ULK1. Compared with WT L02 cells group, the amounts of acetylated lysine combined with ULK1 was decreased. When HDAC2 was downregulated by CAY10683 or shRNA-HDAC2 lentiviral vector, the amounts of acetylated lysine combined with ULK1 were increased. When HDAC2 was upregulated by HDAC2-plasmid lentiviral vector, the amounts of acetylated lysine combined with ULK1 were decreased. During the process, MRT68921 could decrease the amounts of acetylated lysine combined with ULK1. D Then Basepeak of IP/MS qualitative results showed peptide signal strength. E The secondary mass spectrometry displayed ULK1 K68 lysine site was modified by acetylation in L02 cells (the pink words “acK”). F The lysine site of K65, K62, K68, K132, and K162 in kinase domain (KD) area, K806 and K625 in serine/threonine (S/T) domain area were the common acetylation sites for human ULK1 protein. G The space structures of K68 lysine site (in the red box) in human ULK1 protein. The right side is a partial enlarged view of K68 lysine site. Ac-Lys: acetylated lysine.