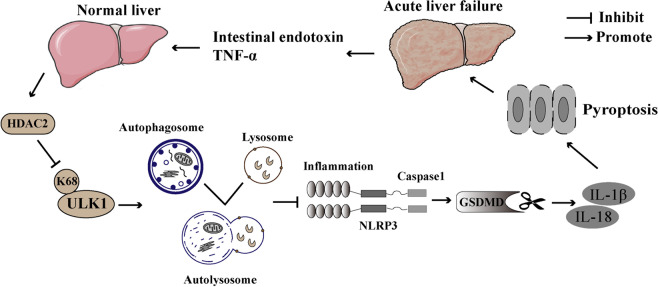
Fig. 7. HDAC2 regulating autophagy via ULK1-NLRP3-pyroptosis pathway to influence the inflammatory responses in acute liver failure.
In the process of ALF, intestinal-derived LPS promotes the secretion of inflammatory factors, such as TNF-α by inflammatory cells in the liver, and further causes a “two-hit” to the liver. During this process, the level of HDAC2 was increased, and the K68 lysine site on the non-histone protein ULK1 will be deacetylated by HDAC2 to reduce its expression. Then ULK1-dependent autophagosomes activate autolysosomes and further promote the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes. Inflammasome can process pro-caspase-1 into mature caspase-1, thereby promote the maturation of IL-1β and IL-18. During this process, the N-terminal GSDMD protein was highly aggregated and binding lipids. Pores are formed on the cell membrane by combination. The cells gradually rupture with a large release of inflammatory factors IL-18 and IL-1β. The released IL-1β and IL-18 further aggravate liver damage during ALF. HDAC2 inhibitors and pyroptosis inhibitors showed the treatment effect on ALF. The K68 lysine site of acetylated non-histone protein ULK1 might be the target for the diagnosis and treatment of ALF. More importantly, the K68 lysine site on ULK1 protein was deacetylated by HDAC2 to provide guarantee for the accurate treatment of ALF with HDAC2 inhibitors in the future.