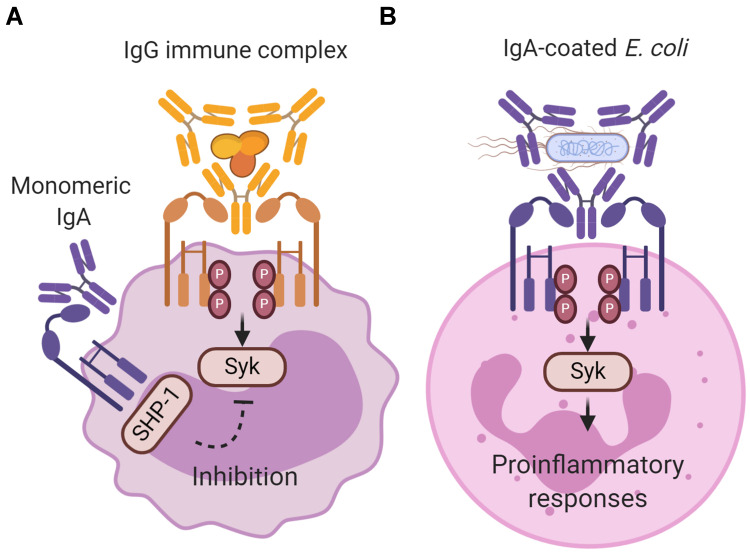
Figure 1.
Inhibitory and activating signaling via FcαRI after ligand binding. (A) Monomeric IgA (not complexed to an antigen) does not induce FcαRI cross-linking resulting in partial phosphorylation of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) and recruitment of Src homology region 2 domain‐containing phosphatase‐1 (SHP‐1). This results in inhibition of ITAM signaling, and impairs phosphorylation of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk), LAT and ERK, which is initiated through signaling via other activating Fc receptors (like IgG-mediated Fcγ receptor activation). The exact binding of free dIgA to FcαRI, and concomitant signaling, has not yet been resolved. (B) IgA immune complexes (eg IgA-coated Escherichia coli) induce cross‐linking of FcαRI, resulting in ITAM phosphorylation of the associated FcR γ-chain. Phosphorylated ITAMs subsequently function as a docking site for signaling molecules such as Syk. Syk plays an essential role in initiating signaling pathways, including the Ras/Raf/MEK/MAPK pathway. Activation of signaling pathways results in pro‐inflammatory cellular functions such as phagocytosis, antibody‐dependent cellular cytotoxicity, respiratory burst, degranulation, antigen presentation, and release of NETS, cytokines and inflammatory mediators. Created with BioRender.com.