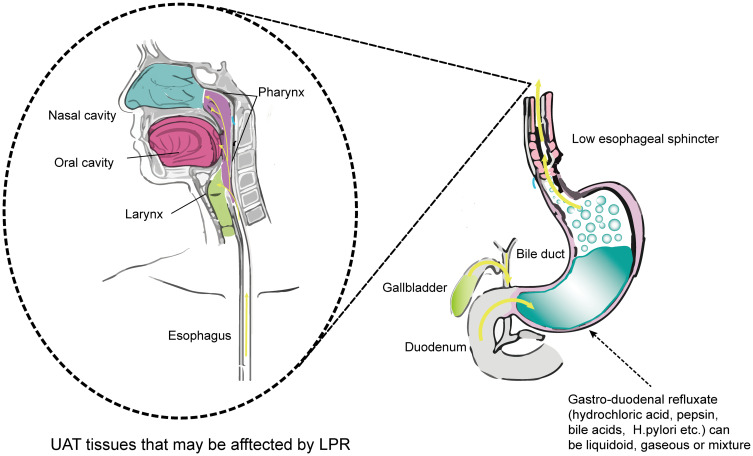
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of LPR and LPR-related symptoms. Dysfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter causes the reflux of gastro-duodenal contents into the UAT mucosa. Reflux mainly injures the mucosa of the larynx and pharynx, but sometimes can even affect the middle ear through the eustachian tube. Refluxate containing multiple acids and proteases injures the UAT mucosa and causes later mucosal inflammation. The left part of Figure 1 has adapted from Douglas College Human Anatomy & Physiology II. Douglas College,New Westminster BC. Aug 31, 2017. Douglas College Human Anatomy and Physiology II (1st ed.) by Rice University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. 126