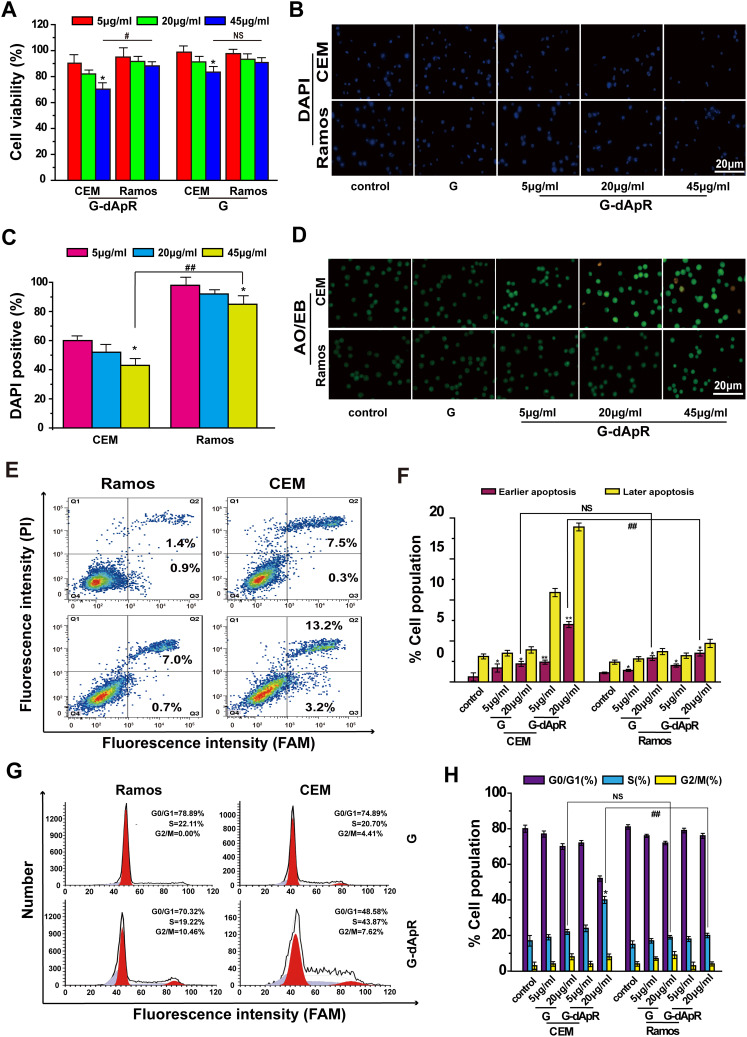
Figure 4.
Inhibition of G-dApR on cell viability by inducing apoptosis. (A) Viability of CEM cells was decreased in a concentration-dependent manner after incubation with G-dApR (5, 20 and 45 μg/mL). (B, C) Fluorescent images (B) and quantitative analysis (C) of DAPI staining of CEM and Ramos cells after incubation with G-dApR (5, 20 and 45 μg/mL). The results showed that G-dApR induced more CEM cells into apoptosis than Ramos cells. (D) AO/EB staining of CEM and Ramos cells after incubation with G-dApR (5, 20 and 45 μg/mL). G-dApR caused more CEM cells to apoptosis (yellow dots) than Ramos cells. (E, F) Annexin V-FITC/PI apoptotic analysis confirmed the stronger dose-dependent apoptosis on CEM cells than Ramos induced by G-dApR. (G, H) Cell cycle distribution of CEM and Ramos cells after exposure to G-dApR. Flow cytometry analysis revealed that G-dApR arrested CEM cells at cell cycle S phase more than Ramos.
Note: G was also measured as the control. NSIndicates no statistical difference, while *,# and **,## represents P < 0.05 and P < 0.01.