Figure 1.
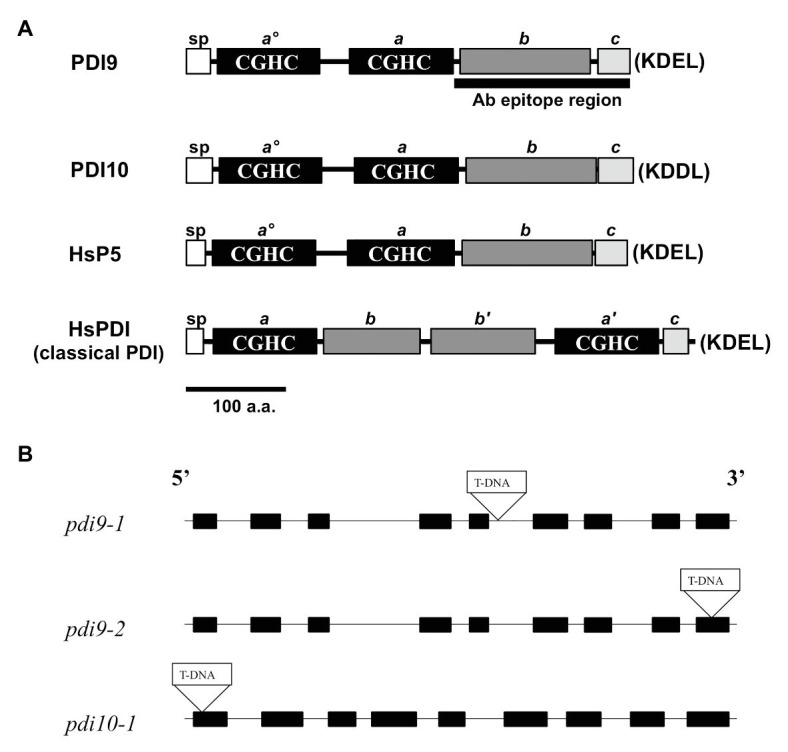
PDI-M subfamily protein domains and mutant gene maps. (A) The primary protein structures and domains of PDI-M subfamily members, PDI9 and PDI10, relative to the domain organization of mammalian classical PDI and P5. SP, signal peptide, thioredoxin (TRX) catalytic sites CGHC (termed ao, a', and a), the TRX fold (b, b'), and acidic (c) domains. The last four residues of each protein (KDEL, KDDL), corresponding to potential ER retention signals, are shown in parenthesis. The black bar, “Ab epitope region,” denotes the less conserved subregion of the PDI9 protein used to make the specific antiserum. (B) The three independent transfer DNA (T-DNA) insertion sites are shown within the gene maps of the pdi9 and pdi10 loci, where black rectangles are exons and intervening connecting lines are introns.
