Figure 4.
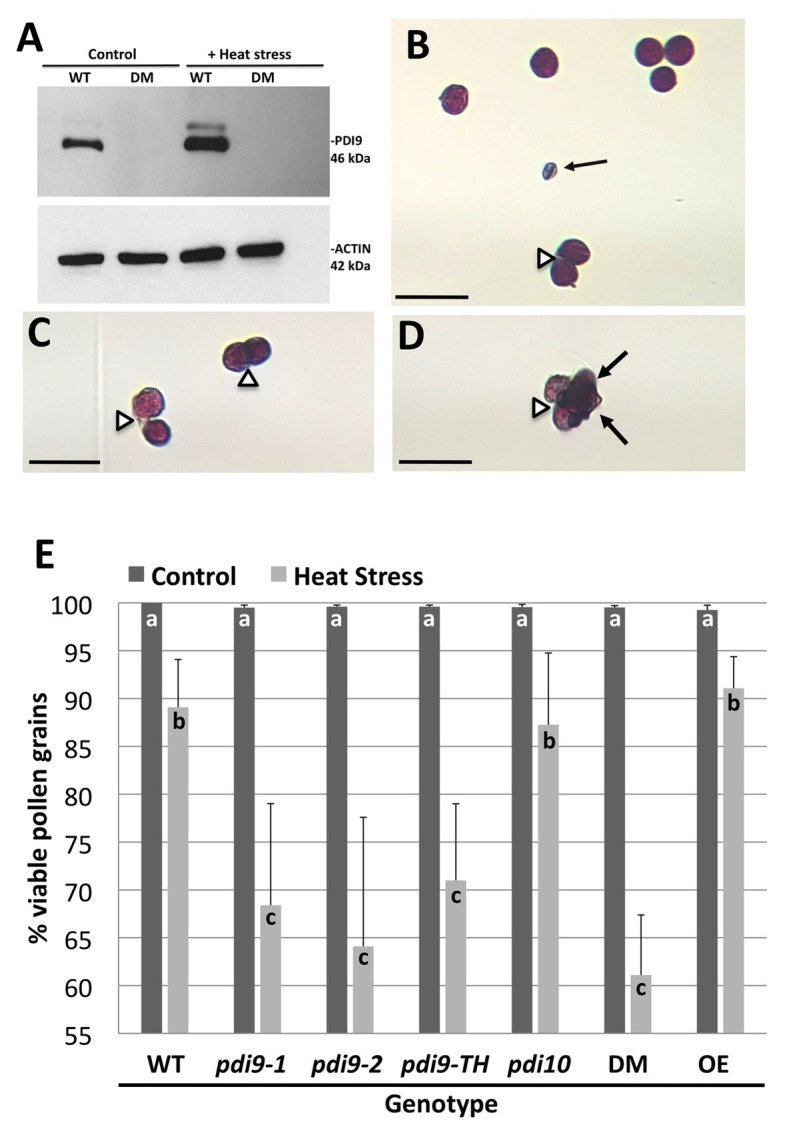
The expression of PDI9 and the effects of PDI9 and PDI10 on the development of healthy pollen in plants exposed to heat stress. (A) Immunoblot analysis using the PDI9-antiserum on pollen proteins from WT, and the 27A pdi9-pdi10 double mutant (DM), exposed to control and heat stress conditions. Alexander staining of pollen grains from WT (B,C) and DM (D) pollen from heat stressed plants. Black arrows point to aborted pollen grains, whereas open arrowheads indicate pollen grains sticking to each other. Scale bars denote 50 microns (B–D). (E) Histogram showing the percent of total viable pollen grains for the single pdi9 (two independent lines) and pdi10 mutants, the pdi9-pdi10 DM, pdi9-1/pdi9-2 transheterozygote mutant line (pdi9-TH) and the PDI9 overexpressor line in untreated (control) and heat-stressed plants. Letters indicate significance between samples (p < 0.05 for n = 6 each genotype treatment for three independent experiments, except pdi9-TH which was two experiments).
