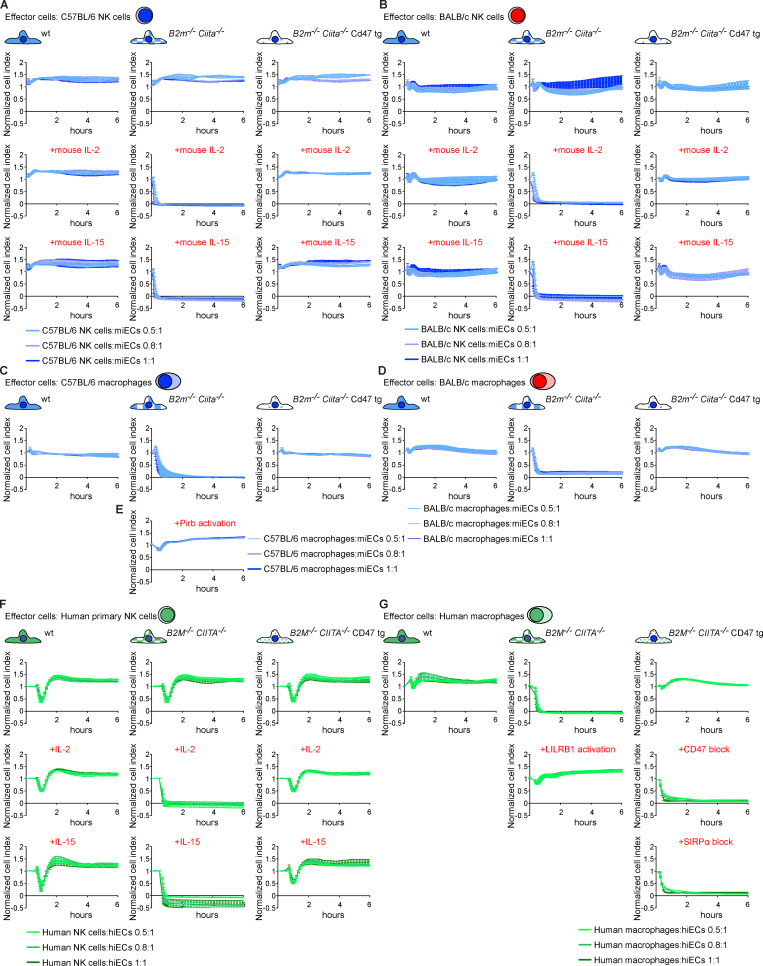
Figure S1.
Cd47 protects MHC-deficient miECs and CD47 protects HLA-deficient hiECs from killing by NK cells and macrophages in vitro. (A–D) WT, B2m−/−Ciita−/−, and B2m−/−Ciita−/− Cd47 tg miECs were challenged with syngeneic C57BL/6 NK cells (A), allogeneic BALB/c NK cells (B), syngeneic C57BL/6 macrophages (C), or allogeneic BALB/c macrophages (D). Where indicated, NK cells were stimulated with mouse IL-2 or IL-15. Graphs show mean ± SD and three independent replicates per group and time point; three different E:T ratios are shown. (E) B2m−/−Ciita−/− miECs were incubated with syngeneic C57BL/6 macrophages treated with an activating anti-Pirb antibody (mean ± SD, three independent replicates per group and time point, and three different E:T ratios are shown). (F and G) WT, B2M−/−CIITA−/−, and B2M−/−CIITA−/− CD47 tg hiECs were challenged with allogeneic human primary NK cells (F) or allogeneic human macrophages (G). Where indicated, NK cells were stimulated with IL-2 or IL-15. Where indicated, an agonist anti-LILRB1 antibody (clone GHI/75) was added to the assay. A specific blocking antibody against CD47 (clone B6.H12) or a blocking peptide against SIRPα was used in some assays. Graphs show mean ± SD and three independent replicates per group and time point; three different E:T ratios are shown. wt, wild-type.