Figure 3. Chronotropic reserve is impaired in aged rats.
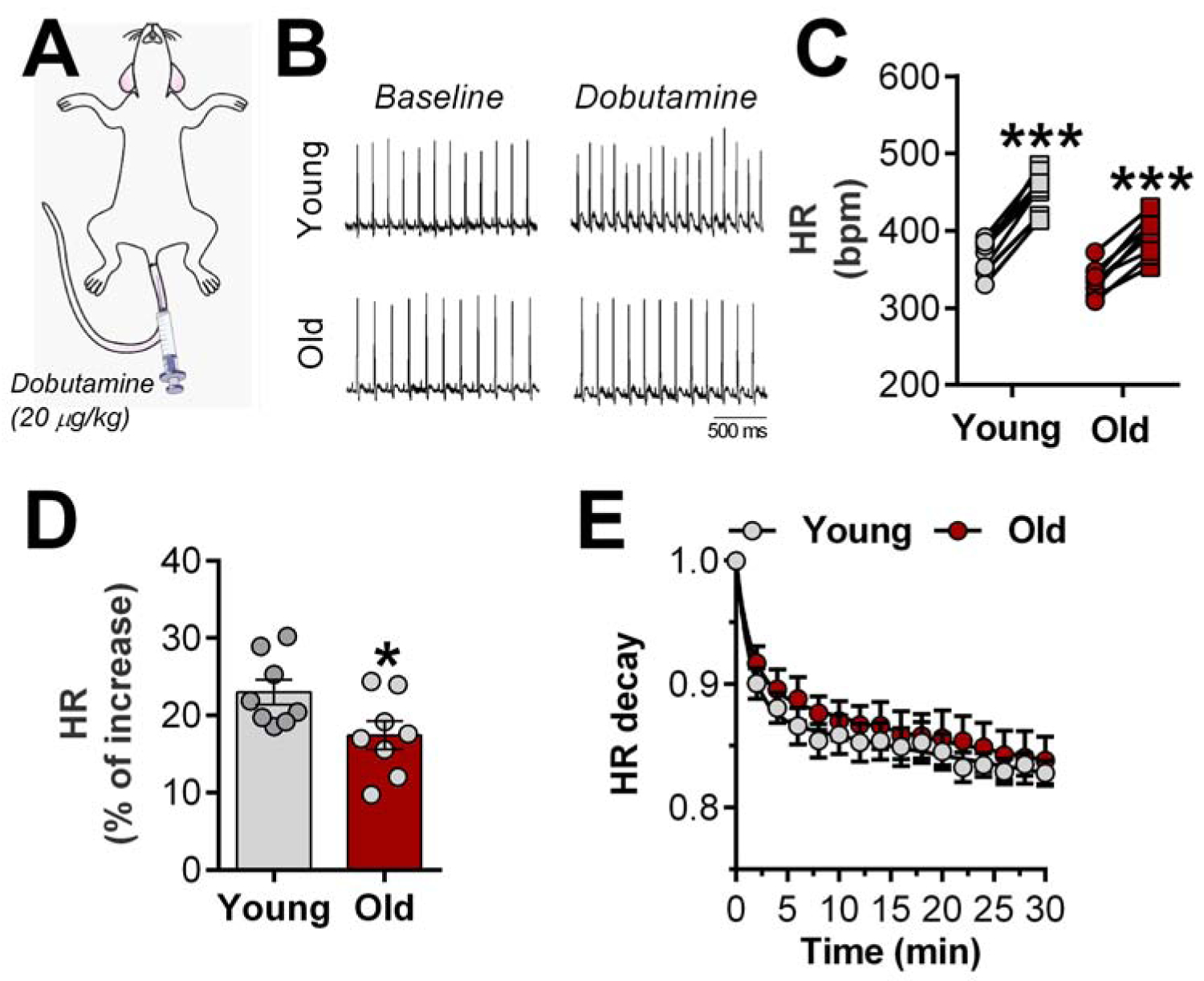
A, In vivo dobutamine stress was used to determine the chronotropic reserve in young and aged animals; Representative ECG recordings (B) and quantification of β-adrenergic-induced heart rate (HR) increase (C, circle: baseline and square: dobutamine-induced HR response); D, β-adrenergic responsiveness in both groups; E, HR recovery time after maximal effect of dobutamine. Data are expressed as individual values (before-after, C) and mean ± SEM. Paired (C) and unpaired Student’s t-test (D). Double-exponential fit of HR decay phase was used. ***P<0.01 vs. baseline and *P<0.05 vs. young females.
