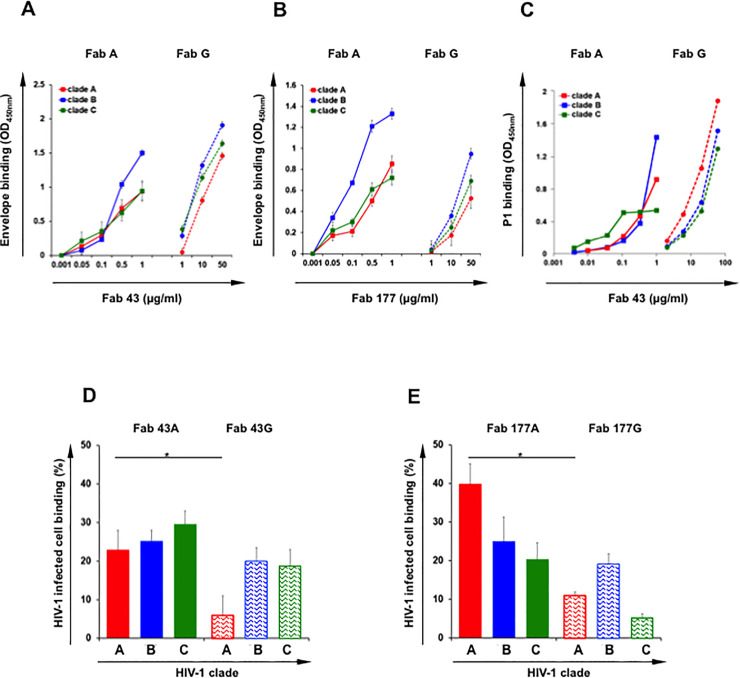
Fig 1.
FabA and G of clones 43 and 177 binding to HIV envelope gp41 clades A, B and C in a dose dependent manner. A and B: The specificity of FabA (solid line) and FabG (dotted line) for clade A gp140 (red), clade B gp41 (blue) clade C gp41 (green) was evaluated by ELISA. For direct comparison of FabA and G isotypes, detection was performed using an anti-kappa light chain. Specific binding (OD450 nm) is plotted as a function of Fab concentration (μg/ml). Values represent mean ± SEM, derived from 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. (A) Fab 43, (B) Fab 177. C: The specificity of FabA 43 (solid line) and FabG 43 (dotted line) for the peptide P1 cross clade, namely clade A (red), clade B (blue) and clade C (green) was evaluated by ELISA. One representative out of three independent experiments performed in duplicate is shown. D and E: Binding of FabA and G of clones 43 and 177 to HIV-1 infected CD4+T-cells. FabA (solid bars) and FabG (hatched bars) from clones 43 (D) and 177 (E) were incubated with Clade A (red) or clade B (blue) and clade C (green) HIV-infected cells or uninfected cells as negative control overnight at 4°C. Irrelevant IgA and IgG were used as negative controls. Specific binding was detected using FITC conjugated anti-human kappa light chain to allow for direct comparison of both FabA and G isotypes, and analyzed by flow cytometry, as indicated in Materials and methods section. Values represent the % of Fab+± SEM among HIV-1-infected (Gag-p24+) CD4+T-cells. Binding of all Fabs to non-infected cells was negligible. Binding of irrelevant IgA and IgG to infected cells it was fixed at 1% and subtracted from the specific binding values; n = 3 independent experiments. Student’s t–test, * = p<0.05.