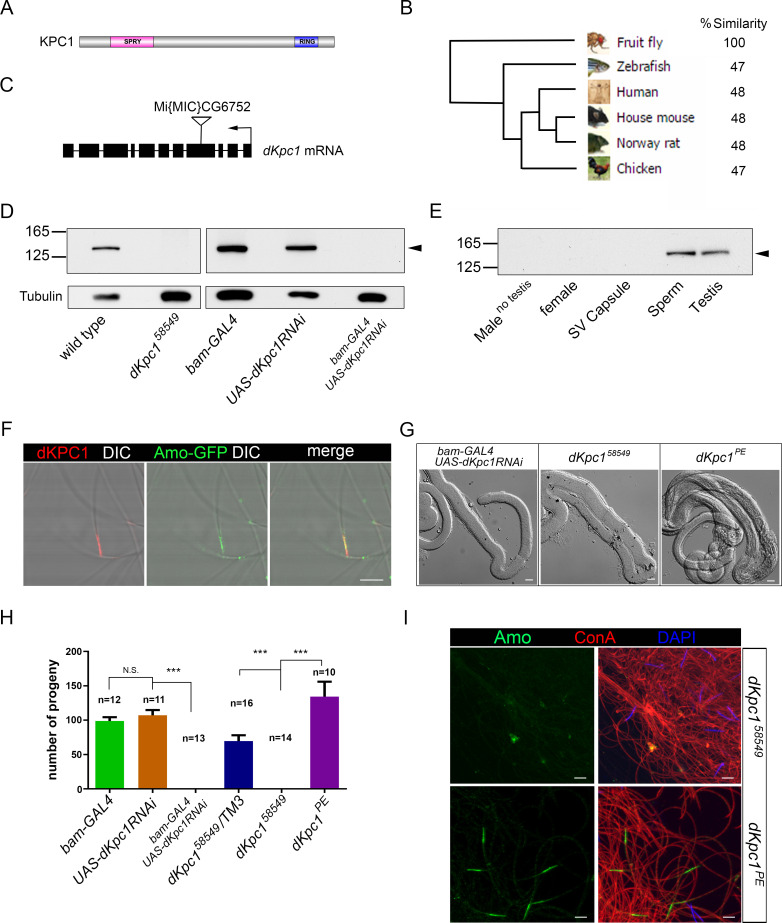
Fig 4. Drosophila Homolog of KPC1 (dKPC1) is required for sperm storage and Amo Localization.
(A) Domain structure of dKPC1 showing an N-terminal SPRY domain and a C-terminal Ring-finger domain. dKPC1 has 1332 amino acids and is predicted to be ~151 kDa in size. (B) Phylogenetic tree demonstrates homology between dKPC1 and related proteins. (C) Map of the CG6752/dKpc1 locus showing the MiMIC transposon insertion (dKpc158549) in Exon 4. Black arrow indicates the direction of transcription. (D-E) Western blots probed with antisera to dKPC1. The antibody detects a single band of ~151 kDa, indicated by the arrowhead, in wild type testes and sperm. There is no dKPC1 detectable in testes dissected from dKpc158549 males, from males with RNAi mediated knock-down of dKpc1, in females or in males lacking testes. (F) Amo-GFP sperm stained with antisera to dKPC1: red and to GFP: green. DIC and fluorescence images are merged showing that the two proteins partially co-localize at the tip of the sperm tail. Scale bars: 5 μm. (G) DIC images of wild type seminal receptacles dissected after mating with males of the indicated genotypes. Receptacles are empty after mating with dKpc158549 males and males with RNAi-mediated knock-down of dKpc1. Sperm storage is rescued after precise excision of the transposon (dKpc1PE). Scale bars: 20 μm. (H) Fertility tests with males of the indicated genotypes mated to wild type females. dKpc158549 males and males with RNAi-mediated knock down of dKpc1 are sterile. Fertility is rescued by precise excision of the MiMIC transposon in dKpc1 (dKpc1PE). The number of tests per genotype is denoted above the bars. ***p< 0.001. N.S. = not significant. (I) Wild type and dKpc158549 sperm stained with anti Amo: green, concanavalin A: red and DAPI: blue. Amo is missing in dKpc158549 sperm tails but localization is rescued by precise excision of the MiMIC transposon (dKpc1PE). Scale bars: 5 μm.