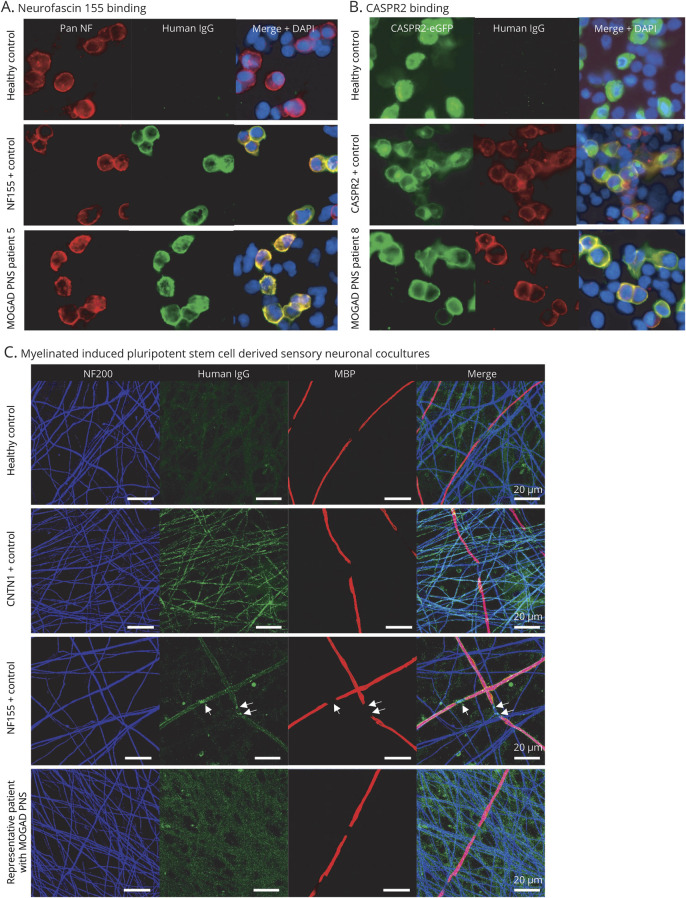
Figure 2. Antibody-associated peripheral nerve involvement.
(A) Human IgG binding (green) colocalizes on the cell surface of HEK293 cells to binding of a commercial pan-neurofascin antibody (red) when cells were incubated with sera from an NF155 positive control and MOGAD PNS patient 5, but not in a healthy control. (B) Human IgG binding (red) colocalizes on the cell surface of HEK293 cells transfected with CASPR2-eGFP (green) when cells were incubated with sera from a CASPR2-positive control and MOGAD PNS patient 8, but not in a healthy control. (C) Images of serum-treated myelinating cocultures labeled with anti-human IgG antibodies (green). Anti-NF200 (blue) and anti-MBP (red) primary antibodies were used to visualize axonal processes and myelin internodes, respectively. This coculture, treated with serum from a healthy control, anti-CNTN1 antibody or anti-NF155 antibody positive controls, and a representative MOGAD PNS patient are shown. Arrows indicate the nodal/paranodal deposition of human IgG. Note lack of specific labeling in healthy control and MOGAD PNS patient serum. CASPR2 = contactin-associated protein-like 2; CNTN1 = contactin 1; DAPI 4′,6-diamidino-2- phenylindole; eGFP = enhanced green fluorescent protein; IgG = immunoglobulin G; MBP = myelin basic protein; MOGAD = myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody–associated disorder; NF = neurofascin; NF155 = neurofascin 155; NF200 = neurofilament 200; PNS = peripheral nervous system.