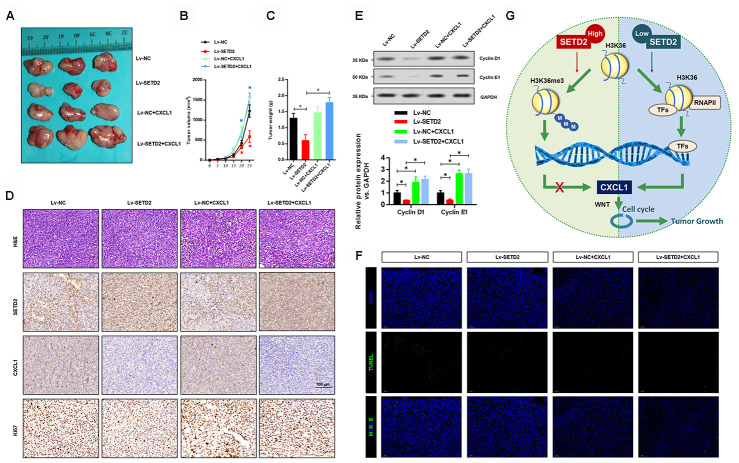
Figure 8.
SETD2 impairs lung cancer cell growth in vivo. (A) A representative image of tumor volume of control and SETD2-overexpressing H1650 cells with or without CXCL1 overexpression. (B) Measurement of subcutaneous tumor growth of control and SETD2-overexpressing H1650 cells with or without CXCL1 overexpression. (C) Subcutaneous tumors were excised and weighed after mice were sacrificed. (D) H&E, SETD2 and CXCL1 staining of subcutaneous tumors of control and SETD2-overexpressing H1650 cells with or without CXCL1 overexpression. Scale bars: 50 μm. (E) Protein levels of G1 phase checkpoints Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E1 upon SETD2 or CXCL1 overexpression in H1650 cells generated xenograft tumors. (F) Apoptosis levels in the H1650 cells generated xenograft tumor were evaluated by TUNEL assay. (G) Graphic model of SETD2 functions in LUAD. SETD2-catalyzed H3K36me3 recruited specific transcription factors to negatively regulate CXCL1 transcription, in which activation of CXCL1 facilitated cell cycle progression, whereas inactivation of CXCL1 led to tumor growth suppression. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. One-way ANOVA with Dunn’s multiple-comparisons test.