Table 2.
Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma according to baseline characteristics
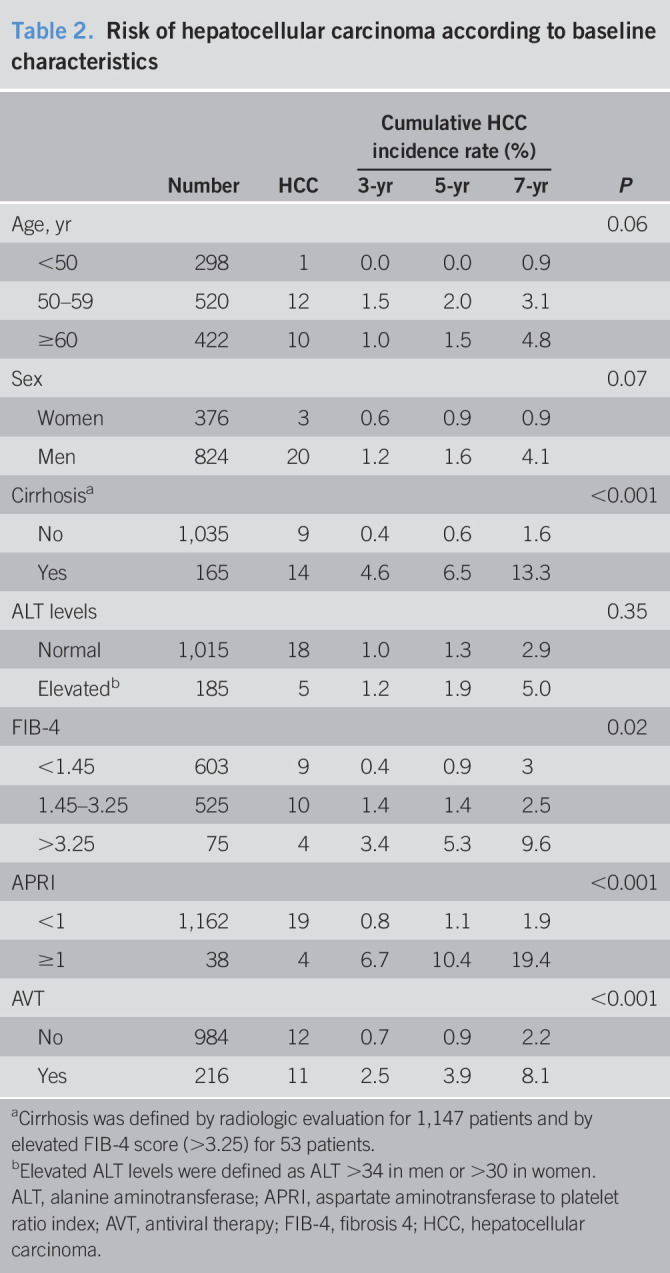
| Number | HCC | Cumulative HCC incidence rate (%) | P | |||
| 3-yr | 5-yr | 7-yr | ||||
| Age, yr | 0.06 | |||||
| <50 | 298 | 1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | |
| 50–59 | 520 | 12 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 3.1 | |
| ≥60 | 422 | 10 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 4.8 | |
| Sex | 0.07 | |||||
| Women | 376 | 3 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | |
| Men | 824 | 20 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 4.1 | |
| Cirrhosisa | <0.001 | |||||
| No | 1,035 | 9 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.6 | |
| Yes | 165 | 14 | 4.6 | 6.5 | 13.3 | |
| ALT levels | 0.35 | |||||
| Normal | 1,015 | 18 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 2.9 | |
| Elevatedb | 185 | 5 | 1.2 | 1.9 | 5.0 | |
| FIB-4 | 0.02 | |||||
| <1.45 | 603 | 9 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 3 | |
| 1.45–3.25 | 525 | 10 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 2.5 | |
| >3.25 | 75 | 4 | 3.4 | 5.3 | 9.6 | |
| APRI | <0.001 | |||||
| <1 | 1,162 | 19 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 1.9 | |
| ≥1 | 38 | 4 | 6.7 | 10.4 | 19.4 | |
| AVT | <0.001 | |||||
| No | 984 | 12 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 2.2 | |
| Yes | 216 | 11 | 2.5 | 3.9 | 8.1 | |
Cirrhosis was defined by radiologic evaluation for 1,147 patients and by elevated FIB-4 score (>3.25) for 53 patients.
Elevated ALT levels were defined as ALT >34 in men or >30 in women.
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; APRI, aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index; AVT, antiviral therapy; FIB-4, fibrosis 4; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.
