Figure 1.
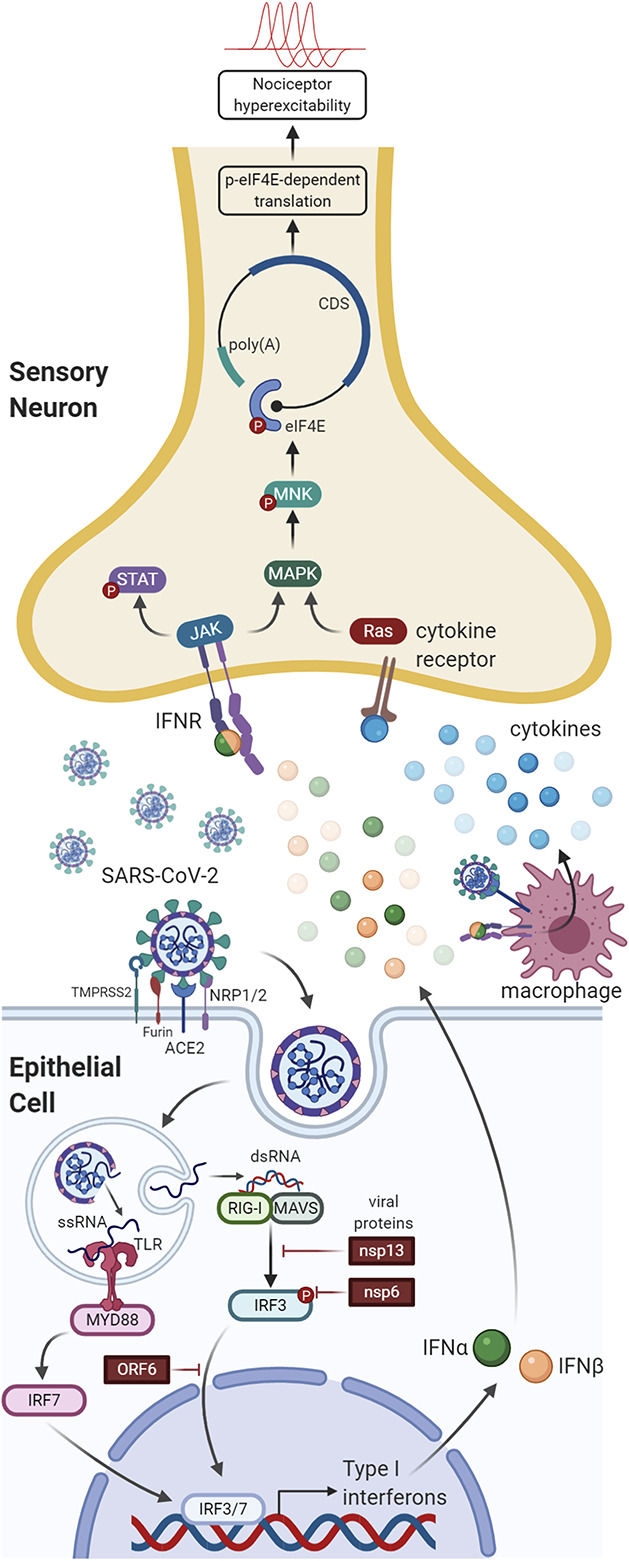
Cellular response to SARS-CoV-2 infection in the lung and its relationship to nociceptors. The cleavage of viral S protein by surface proteins such as TMPRSS2 and furin facilitates SARS-CoV-2 entry into lung epithelial cells through the ACE2 receptor. Neuropilin 1 and 2 (NRP1/2) act as additional viral entry factors. Viral RNA activates interferon regulatory factors (IRF3 and IRF7) that promote type I interferon (IFNα/β) production. The binding of type I IFNs to IFN receptors on pulmonary nociceptors is postulated to stimulate MNK-mediated eIF4E phosphorylation, resulting in nociceptor sensitization. When the viral load is high, viral proteins (NSP13, NSP6, and ORF6) suppress IFN production, contributing to evasion of type I IFN production and increasing the severity of COVID-19. ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.
