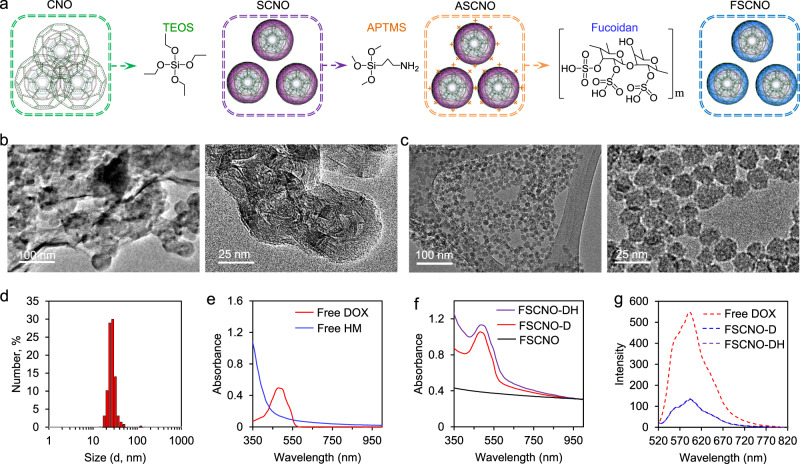
Fig. 2. Synthesis and characterization of nanoparticles.
a A schematic illustration of the procedure for preparing the silica-carbon nano-onion (SCNO) nanoparticles using carbon nano-onions (CNOs) and tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), modifying the SCNO nanoparticles with (3-Aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane (APTMS) to form ASCNO nanoparticles, and coating the ASCNO nanoparticles with fucoidan to produce the FSCNO nanoparticles. b, c Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of the CNOs (b) and FSCNO nanoparticles (c). d Size (in diameter) distribution of the FSCNO nanoparticles determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS) at room temperature. e UV-Vis absorbance of free doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) in deionized water and HM30181A (HM) in DMSO solution showing DOX has an absorbance peak at 485 nm while HM has strong absorption around 350 nm. f UV-Vis absorbance of FSCNO-D nanoparticles in deionized water showing an absorbance peak of DOX and FSCNO-DH in deionized water nanoparticles showing high absorbance at ~350 nm, suggesting the successful encapsulation of DOX and HM. g Fluorescence spectrophotometry of FSCNO-D and FSCNO-DH nanoparticles together with free DOX showing successful encapsulation of DOX in the two nanoparticles with a fluorescence peak at ~590 nm.