Figure 1: RACK1-FLAG is incorporated into polysomes.
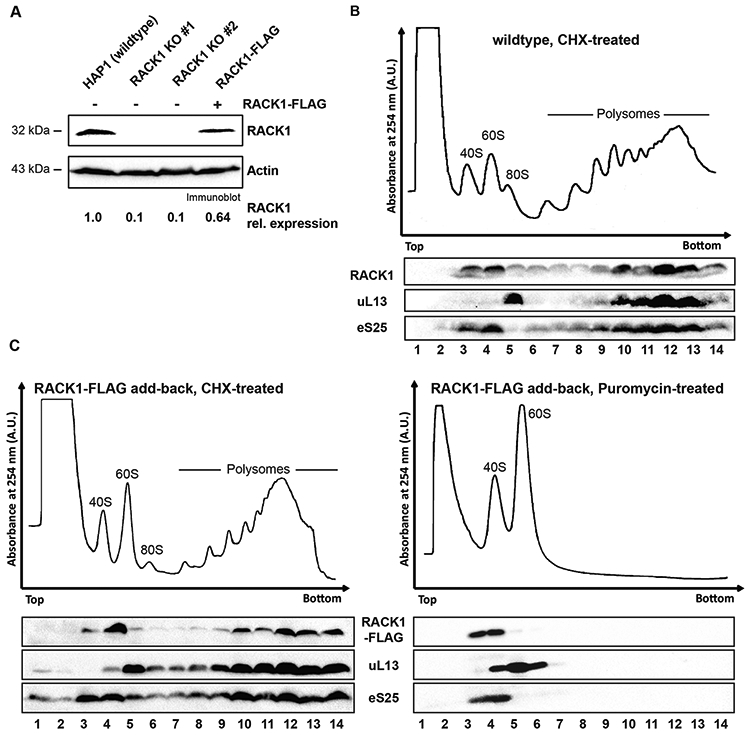
(A) RACK1 levels can be partially restored in RACK1 KO cells by expression of RACK1-FLAG. RACK1 levels were quantified by immunoblot analysis of RACK1 and the loading control actin. (B) Polysome trace of HAP1 wildtype cells and distribution of the ribosomal proteins RACK1, eS25 and uL13 in the gradients. Cell lysate was separated in 10-50% sucrose gradient and absorbance at 254 nm was measured. Proteins from all gradient fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting All ribosomal proteins sediment in fractions according to the distribution of ribosomal subunits and polysomal fractions in the trace. (C) Sucrose gradient analysis of FLAG-tagged RACK1 protein. In cells treated with the translation elongation inhibitor cycloheximide, RACK1-FLAG, detected by immunoblotting using an anti-FLAG antibody, co-sediments with polysomes (fractions 9-14). Upon treatment of cell lysate with the translation elongation puromycin, which separates actively translating ribosomes into the ribosomal subunits, RACK1-FLAG co-sediments with 40S ribosomal subunits in lighter sucrose gradient fractions (fractions 3-4). Immunoblot analysis for eS25 and ul13 are used as indicators for sedimentation of protein components of the small and large ribosomal subunits, respectively.
