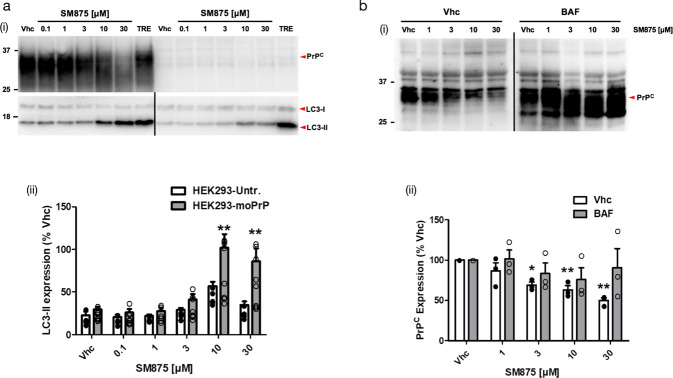
Fig. 4. SM875 decreases PrP level via the autophagy-mediated lysosomal degradation.
a (i) PrP-transfected or untransfected HEK293 cells were treated with different concentrations of SM875 or vehicle (0.1% DMSO, volume equivalent) and the levels of PrP, LC3-I, and LC3-II were evaluated by western blotting (indicated by the red arrowheads). As a positive control, cells were treated with 100 μM trehalose (TRE), a disaccharide previously reported to induce autophagy. (ii) Graphs show the densitometric quantification of LC3-II from independent replicates (n = 8 for PrP-expressing HEK293 cells; n = 5 for untransfected HEK293 cells). Each signal was normalized on the corresponding total protein lane (detected by UV) and expressed as the percentage of vehicle (Vhc)-treated controls (**p < 0.01, by one-way ANOVA test). b (i) ZR-75 cells were treated with different concentrations of SM875 in the presence or absence of autophagy–lysosomal inhibitor bafilomycin A1 (BAF, 10 μM) and PrP levels were evaluated by western blotting. (ii) Graphs show the densitometric quantification of full-length PrP from independent replicates (n = 3). Each signal was normalized on the corresponding total protein lane (detected by UV) and expressed as the percentage of vehicle (Vhc)-treated controls (**p < 0.01, by one-way ANOVA test).