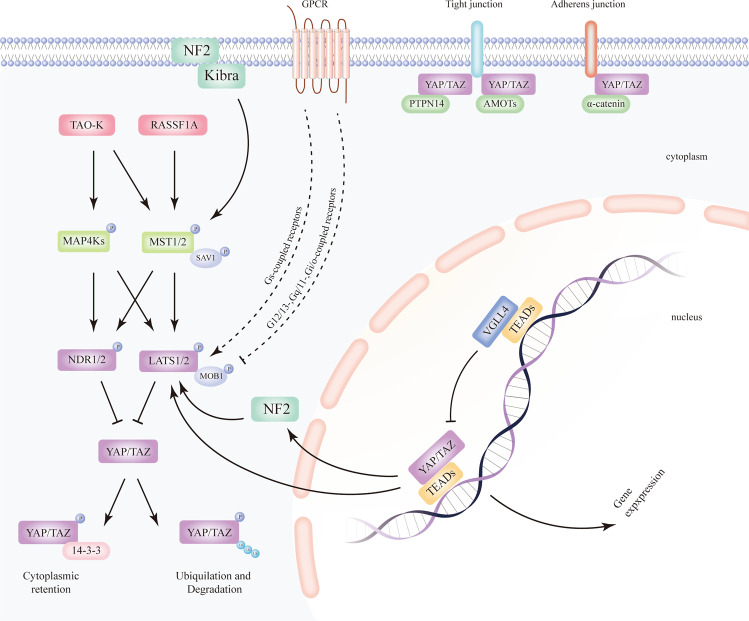
Fig. 1. Regulation of the mammalian Hippo pathway.
The core components of the Hippo pathway encompass MST1/2 and LATS1/2, whereas YAP/TAZ are two major effectors of this pathway. Traditionally, upstream signals turn on the Hippo pathway by phosphorylating and activating MST1/2 as well as the scaffold protein SAV1, followed by phosphorylation and activation of LATS1/2 and the scaffold protein MOB1, thereby preventing YAP/TAZ from translocating to the nucleus and initiating gene expression via binding to TEADs. VGLL4, a transcriptional co-repressor, competes with YAP/TAZ for TEADs binding. Instead, phosphorylated YAP/TAZ are isolated in the cytoplasm through interaction with protein 14-3-3 or experience ubiquitylation and degradation. Expanded Hippo pathway encompasses MAP4Ks as well as NDR1/2. MAP4Ks function similarly as MST1/2, performing activating phosphorylation of LATS1/2 and/or NDR1/2, consequently leading to the inhibition of downstream YAP/TAZ via LATS1/2- or NDR1/2-regulated phosphorylation. The complex of YAP/TAZ and TEADs can both directly enhance the function of LATS2 and indirectly stimulate LATS1/2 expression via NF2, which constitute a feedback loop. Independent of the upstream kinases, YAP/TAZ may be directly sequestered at cell junctions via interacting with PTPN14, AMOTs, and α-catenin. NF2, Kibra, RASSF1A, and TAO-K stimulated by upstream stimuli, may phosphorylate and activate MST1/2 and/or MAP4Ks. GPCRs may inhibit and enhance LATS1/2 depending on the types of receptors. Arrows, blunt ends, and dotted lines indicate activation, inhibition, and possible regulatory effect, respectively. MST1/2, mammalian sterile 20-like 1/2; SAV1, salvador; LATS1/2, large tumour suppressor homologue 1/2; MOB1A/B, MOB kinase activator 1A/B; YAP, yes-associated protein; TAZ, transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif; NF2, neurofibromin2/Merlin; TAO-K, thousand and one amino acid protein kinase; MAP4Ks, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase; TEAD, transcriptional enhancer associated domain; VGLL4, vestigial-like family member 4; PTPN14, protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 14; AMOT, angiomotin.