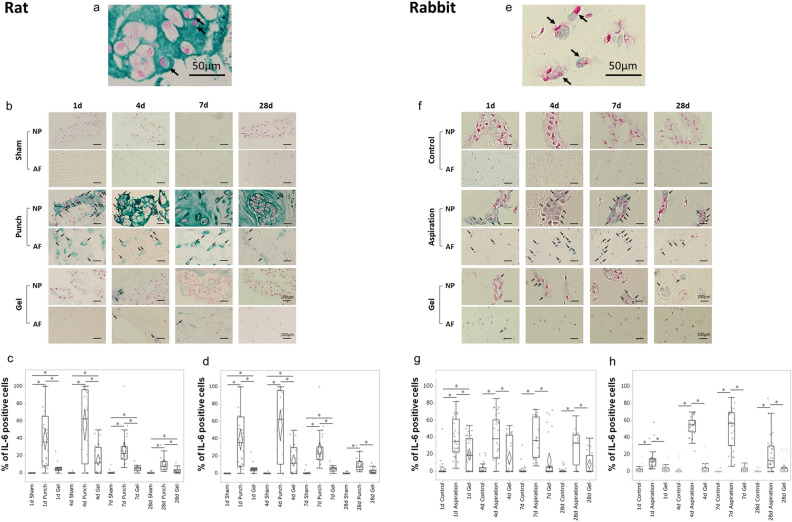
Figure 3.
UPAL gel inhibits interleukin-6 (IL-6) production in rat and rabbit intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration models. The rat nucleus pulposus (NP) punch (a–d) and rabbit NP aspiration (e–h) models were used for immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis to detect the IL-6 levels 1, 4, 7, and 28 days after surgery. The number of IL-6-positive cells in each staining was calculated as a percentage of the number of total NP or annulus fibrosus (AF) cells in five independent, randomly selected fields per disc. IL-6-positive cells are stained green, and nuclei was stained red. (a) Representative image of IL-6-positive NP cells in the rat model (allows). Scale bar, 50 µm. (b) Representative IHC staining for IL-6 1, 4, 7, and 28 days after surgery in rat NP and AF tissues. Arrows indicate IL-6-positive cells. Scale bar, 100 µm. Percentage of IL-6-positive cells in rat NP tissue (c) and AF tissue (d). (e) Representative image of IL-6-positive NP cells in the rabbit model (arrows). Scale bar, 50 µm. (f) Representative IHC staining for IL-6 1, 4, 7, and 28 days after surgery in the rabbit NP and AF tissues. Arrows indicate IL-6-positive cells. Scale bar, 100 µm. Percentage of IL-6 positive cells in rabbit NP tissue (g) and AF tissue (h). The percentages of IL-6-positive NP and AF cells in the gel group were significantly lower than those in the punch group or aspiration at each time point in the rat or rabbit model, respectively (*P < 0.05). The boxes represent the median and the interquartile range, with the vertical lines showing the range. The rhombus shape represents the 95% confidence interval (at each time point, n = 3 rats; n = 6 IVDs in each group).