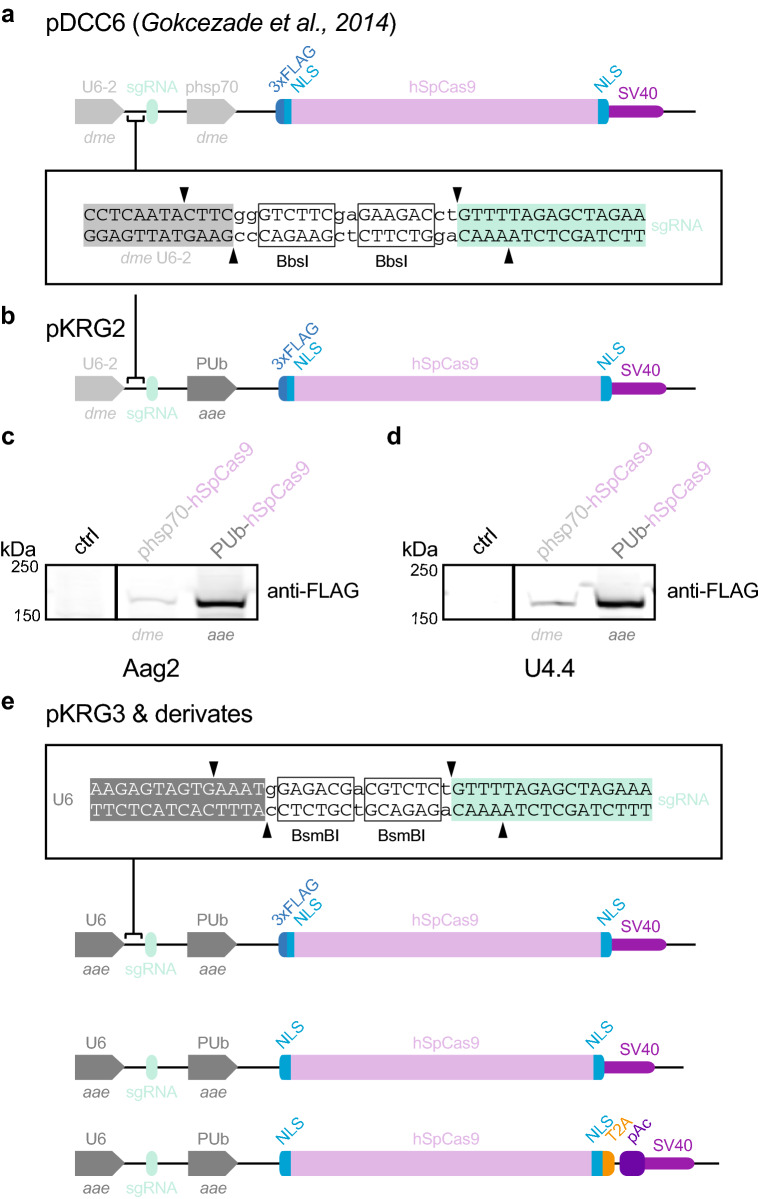
Figure 1.
Mosquito optimized CRISPR/Cas9 plasmids. (a) pDCC6 plasmid published in Gokcezade et al.29. The dme U6-2 promoter drives sgRNA transcription and the dme phsp70 promoter drives expression of a 3xFLAG-tagged hSpCas9. Guide RNAs are cloned by BbsI digest. (b) pKRG2 plasmid, generated by replacing the dme phsp70 promoter with the aae PUb promoter. Cloning of guide RNAs as in (a). (c) Immunoblot of Aag2 cells treated with transfection reagent (ctrl) or transfected with pDCC6 (3xFLAG-hSpCas9; expressed from the dme pshp70 promoter) or with pKRG2 (3xFLAG-hSpCas9; expressed from the PUb promoter). kDa = kilodaltons. Full-length blots in Supplementary Fig. 4. (d) As in (c) for U4.4 cells. (e) To generate pKRG3 mosquito adapted plasmids, the pKRG2 guide RNA cloning site was redesigned to use BsmBI (allowing insertion of the aae U6 promoter, which is incompatible with the BbsI sgRNA cloning site). The RNA Pol II aae U6 promoter was then inserted to express sgRNAs. This plasmid was further modified by removing the N-terminal 3xFLAG from hSpCas9 and adding a T2A-pAc to allow puromycin selection to yield several options for mosquito optimized CRISPR/Cas9 editing.