Figure 6.
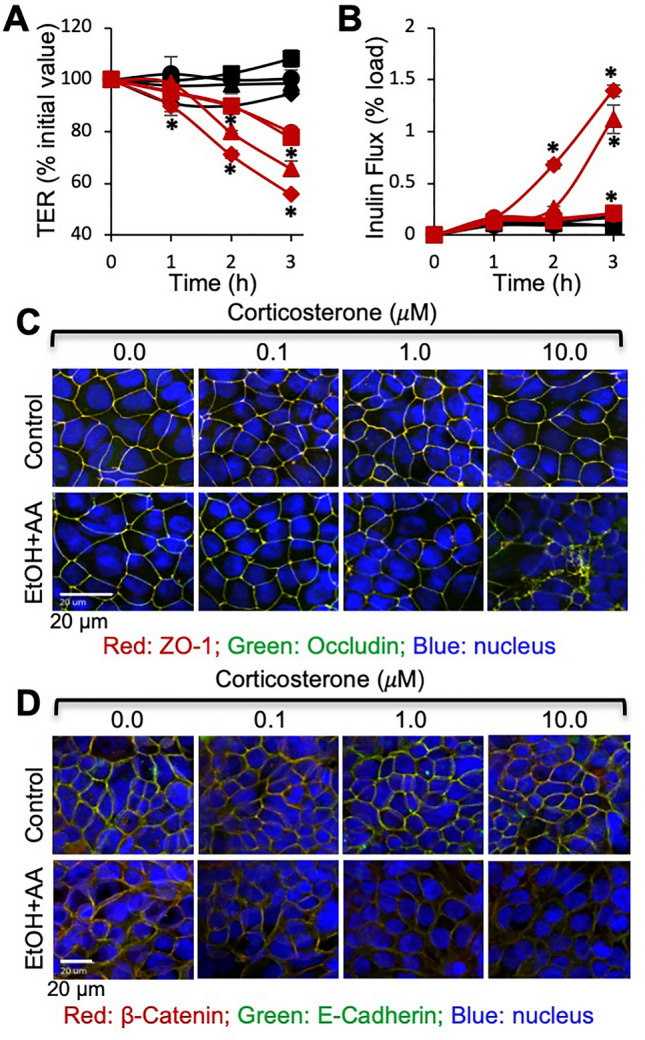
Corticosterone sensitizes Caco-2 cell monolayers for ethanol and acetaldehyde-induced tight junction disruption and barrier dysfunction. Caco-2 cell monolayers were pretreated with varying concentrations (black circle, red circle 0 μM, black square, red square 0.1 μM, black triangle, red triangle 1.0 μM, black diamond, red diamond 10 μM) of corticosterone (CORT) for 24 h, followed by incubation with (red circle, red square, red triangle, red diamond) or without (black circle, black square, black triangle, black diamond) ethanol (20 mM) and acetaldehyde (100 μM) (EtOH + AA). At varying times, TER (A) and FITC-inulin permeability (B) were measured. At 3 h of incubation, cell monolayers were fixed and co-stained for occludin and ZO-1 (C) or E-cadherin and β-catenin (D). Values in graphs are mean ± SEM (n = 6). Asterisks indicate the values that are significantly (P < 0.05) different from corresponding values for groups without ethanol and acetaldehyde treatments.
