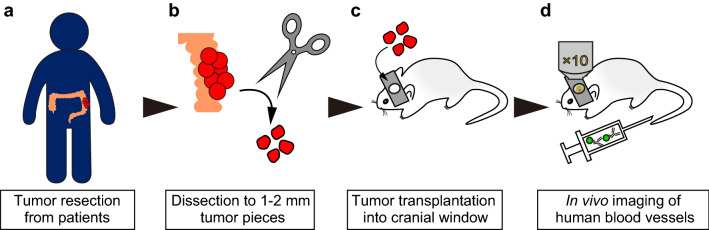
Figure 1.
Development of a continuous imaging model of human blood vessels using human tumor tissues. (a) Human tumor was freshly resected from cancer patients. (b) Tumors were cut into 1–2 mm fragments with scissors. (c) Tumor fragments were transplanted into a cranial window in NOD-Scid mice. (d) Mice were intravenously injected with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-human CD31 monoclonal antibody (huCD31-AF488 Ab) to visualize the human blood vessels specifically in vivo. AF488-labeled human blood vessels were observed by confocal microscopy under isoflurane anesthesia.