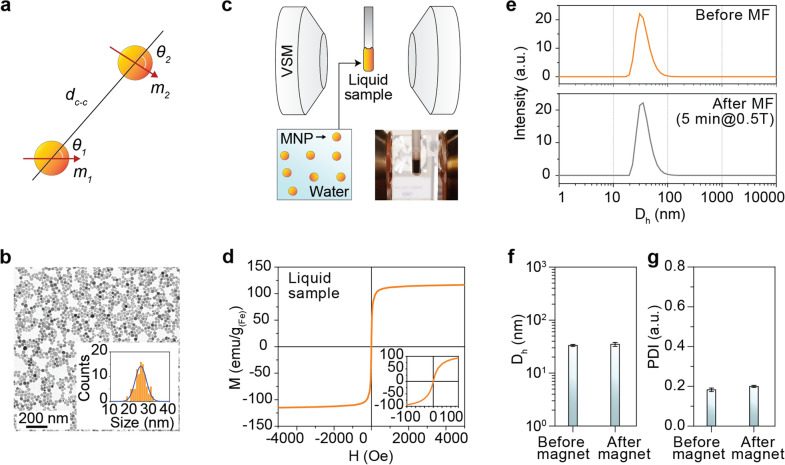
Figure 1.
Dipole–dipole interaction model and nanofluid characterization. (a) A schematic model of dipole–dipole interaction between two SPNPs. dc–c, m, and θ represent center-to-center interparticle distance, the magnetic moment of each MNP, and angle between tow dipole induced by the SPNPs, respectively. (b) A TEM image of 25 nm Mgx–γFe2O3 SPNP (inset, the size distribution of Mgx-γFe2O3 SPNP measured from TEM image). (c) A liquid VSM measurement of magnetic properties of Mgx-γFe2O3 nanofluids. (inset, a picture of Mgx–γFe2O3 nanofluid sample mounted on the VSM holder). (d) M–H major loop of Mgx–γFe2O3 nanofluids measured at the sweeping field of ± 5 kOe (inset, minor M–H loop). (e) The hydrodynamic sizes before (top) and after (bottom) applied HDC,appl (5 min@0.5 T). (f,g) Measured hydrodynamic size (f) and polydispersity index (PDI, g) of the nanofluids before and after the applied HDC,appl.