Fig. 3.
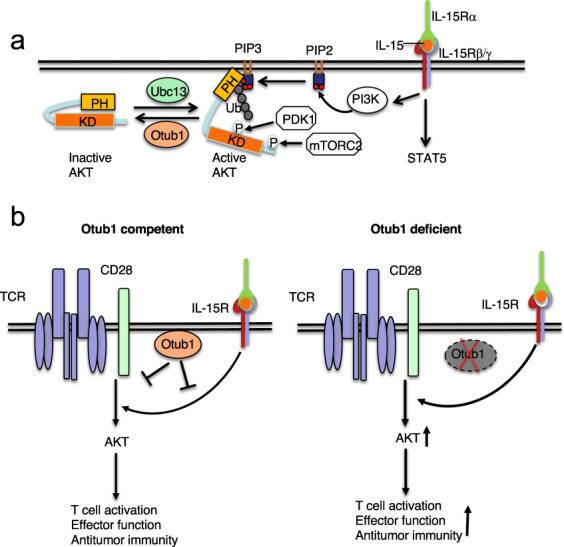
Otub1 serves as a checkpoint of IL-15-mediated CD8 T cell priming by deubiquitination of AKT. a, IL-15 stimulates PI3K activation and AKT K63 ubiquitination, both being required for AKT activation. AKT ubiquitination facilitates its binding to PIP3, probably through a conformational change leading to exposure of the PH domain of AKT, which recruits AKT to the membrane compartment, where AKT is phosphorylated and activated by the kinases PDK1 and mTORC2. Otub1 negatively regulates AKT activation through inhibiting its ubiquitination. b, IL-15 signal primes CD8 T cells for antigen stimulation, which is controlled by Otub1. In response to IL-15 stimulation, Otub1 is recruited to the membrane compartment, where it inhibits AKT activation induced by both IL-15 and TCR/CD28 signals. Otub1 thus functions as a checkpoint molecule regulating IL-15-mediated CD8 T cell priming. Deficiency in Otub1 causes increased AKT signaling and enhanced CD8 T cell responses in cancer immunity
