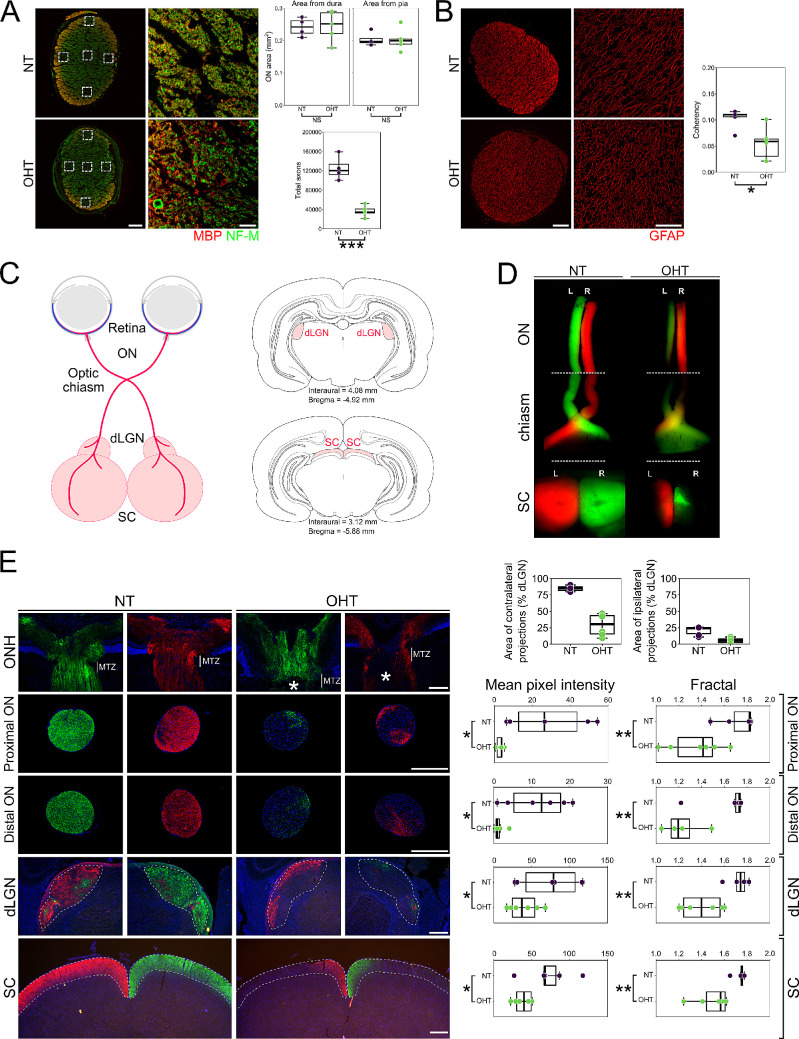
Figure 2.
OHT results in axon degeneration and deficits in axoplasmic transport. (A) Total axon number was assessed in optic nerve sections by high-resolution imaging of NF-M-positive axon fibers and myelin bundles (n = 4 NT nerves; n = 5 OHT nerves). The estimated total number of axons in NT optic nerves (average, 125,000) matched that reported in the literature for adult Brown Norway rats33 and was significantly reduced in OHT eyes. The reduction is likely an overestimate due to an increased number of dystrophic axons in OHT optic nerves that may mask individual small caliber axons. There were no gross changes to optic nerve total size (as measured from the dura or pia mater), but there was a significant loss of RGC axons. Scale bars: 100 µm (left panels); 10 µm (right insets). (B) OHT results in significant remodeling of optic nerve astrocytes (a decrease in fiber alignment and coherency as assessed by OrientationJ). Scale bars: 100 µm (left panels); 50 µm (right insets). (C) Axoplasmic transport was assessed by two-color CT-β tracing from the retina to the terminal visual thalami (dLGN and SC; n = 3 bilateral NT animals; n = 3 bilateral OHT animals). A schematic showing RGC trajectories and visual thalami is shown. OHT results in an absence of axoplasmic transport to terminal regions assessed by both low-power flat-mount SCs (D) and in cryosections (E), based on mean pixel intensity and fractal analysis (for both NT and OHT, n = 6 eyes, n = 6 optic nerves, n = 6 dLGN hemispheres, n = 6 SC hemispheres). Scale bars: 100 µm (ONH); 500 µm (ON, dLGN, SC). Axoplasmic transport was primarily stalled within the optic nerve head (asterisk in E; at the site of the myelin transition zone [MTZ]), resulting in partial transport through the optic nerve to the dLGN and SC. Optic nerves were assessed both proximal to the eye and proximal to the chiasm. The dLGN and SC were assessed in three sections representing rostral, medial, and caudal dLGN or SC, respectively (and expressed as a mean). Both contralateral and ipsilateral projections were reduced in the dLGN (as a percentage of total dLGN area), indicating axonal transport disruption to both hemispheres from a single OHT eye. All panels in a single column (i.e., NT or OHT) are from the same visual tract. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; NS, non-significant (P > 0.05). ON, optic nerve; ONH, optic nerve head.