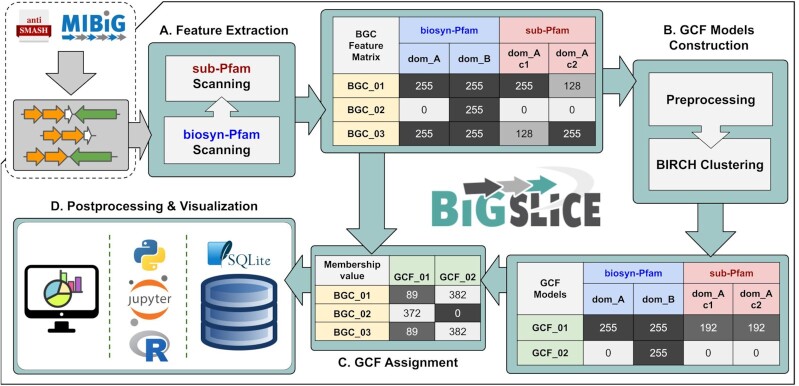
Figure 1:
An overview of BiG-SLiCE's GCF analysis workflow. Taking an input of region/cluster GenBank files from antiSMASH and MIBiG, (A) BiG-SLiCE converts BGCs into numerical feature vectors, which are used to (B) construct the GCF models (cluster centroids) and (C) calculate BGC-to-GCF membership values. Processed data and results are all stored in a file-based SQL database (using SQLite3 [42]), which can then be used (D) to perform further analysis (via external scripts) or to visualize the result in a user-interactive application.