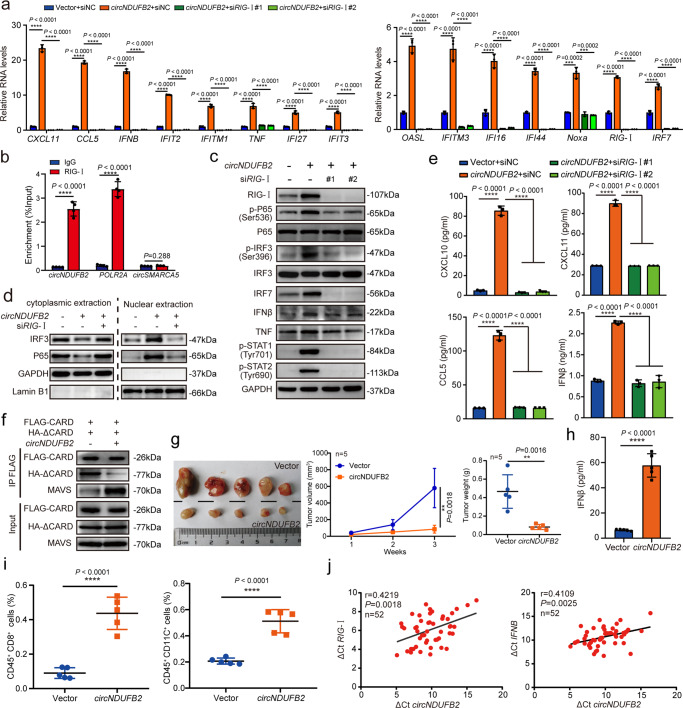
Fig 6. circNDUFB2 activates downstream signaling of RIG-I.
a Fold change of indicated mRNAs in A549 cells with or without RIG-I knockdown. n = 3 biologically independent samples. b Analysis for circNDUFB2 enrichment. RIP assay was performed using RIG-I antibody in A549 cells. POLR2A was used as a positive control and circSMARCA5 was used as a negative control. n = 4 biologically independent samples. c Protein levels in A549 cells with circNDUFB2 overexpression or RIG-I knockdown. d Protein levels of IRF3 and P65 in the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions in the indicated cells. e Levels of CXCL10, CXCL11, CCL5, and IFNβ in the supernatants of A549 cells with circNDUFB2 overexpression or RIG-I knockdown. n = 3 biologically independent samples. f Interactions between CARDs of RIG-I with helicase domain of RIG-I and MAVS in A549 cells. FLAG-CARD, CARDs of RIG-I with FLAG-tagged; HA-ΔCARD, helicase and CTD of RIG-I with HA-tagged. g The volume and weight of subcutaneous xenograft tumors (n = 5 mice per group). h Levels of IFNβ in the serum of mice (n = 5 mice per group). i The percentage of CD8+ T cells and DCs in subcutaneous xenograft tumors. n = 5 tumors per group. j Correlation analysis for circNDUFB2 and RIG-I or IFNβ in the tumorous tissues of 52 NSCLC patients. ΔCt values were normalized according to GAPDH. n = 52 biologically independent NSCLC tissues. R represents the Pearson correlation coefficient. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. P values are calculated by unpaired two-sided t-test in a, b, e, g–i. P values in j are calculated by F-test. Two independent experiments were carried out with similar results in c, d, f.