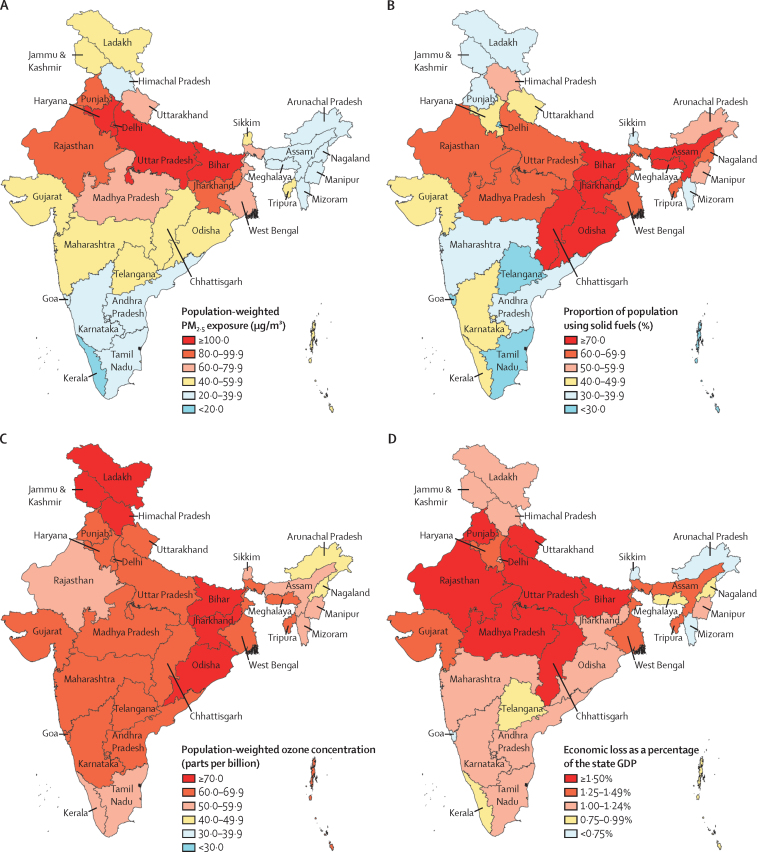
Figure 1.
Exposure to air pollution and economic loss due to premature deaths and morbidity attributable to air pollution in the states of India, 2019
(A) Population-weighted mean ambient PM2·5 concentration. (B) Proportion of population using solid fuels. (C) Population-weighted ozone concentration in parts per billion. (D) Economic loss due to premature deaths and morbidity attributable to air pollution as a percentage of the state GDP. GDP=gross domestic product. PM2·5=fine particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter of 2·5 μm or less.