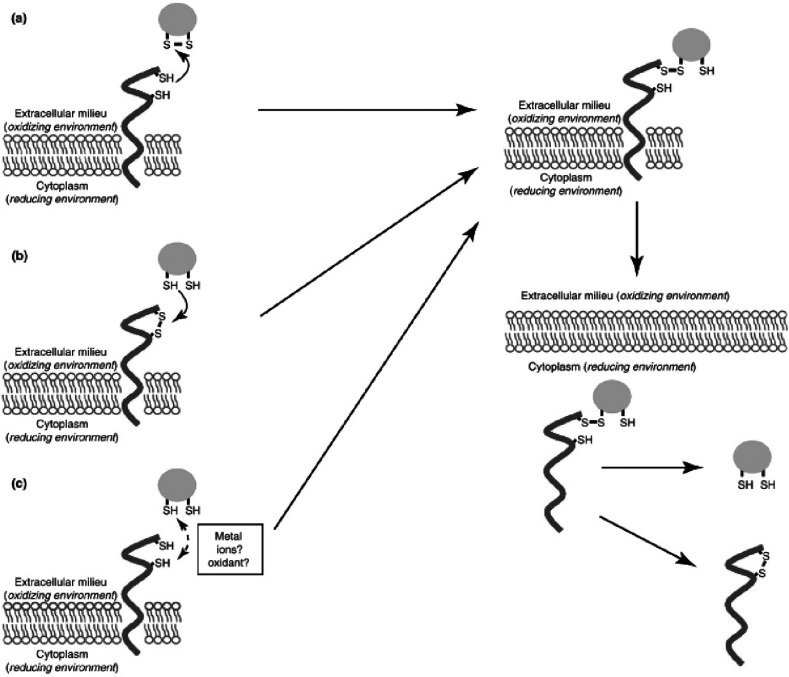
Figure 8.
Potential mechanisms of thiolated chitosan drug carriers reacting with proteins displaying exofacial thiol groups. (a) A disulfide bond exchange reaction between a reactive thiol group at the cell surface and a disulfide bond of the vector takes place. (b) Again a disulfide bond exchange reaction occurs whereby this time a thiol group of the carrier attacks a disulfide bond of the protein. (c) Formation of a disulfide bridge between a thiol group of the vector and an exofacial thiol group of a protein. Metal ions or oxidizing agents can enhance this reaction. Each time a mixed disulfide complex emerges, it is internalized and subsequently reduced within the endosome or cytoplasm, resulting in release of the carrier. Reprinted with permission from ref (163). Copyright 2012 Elsevier.