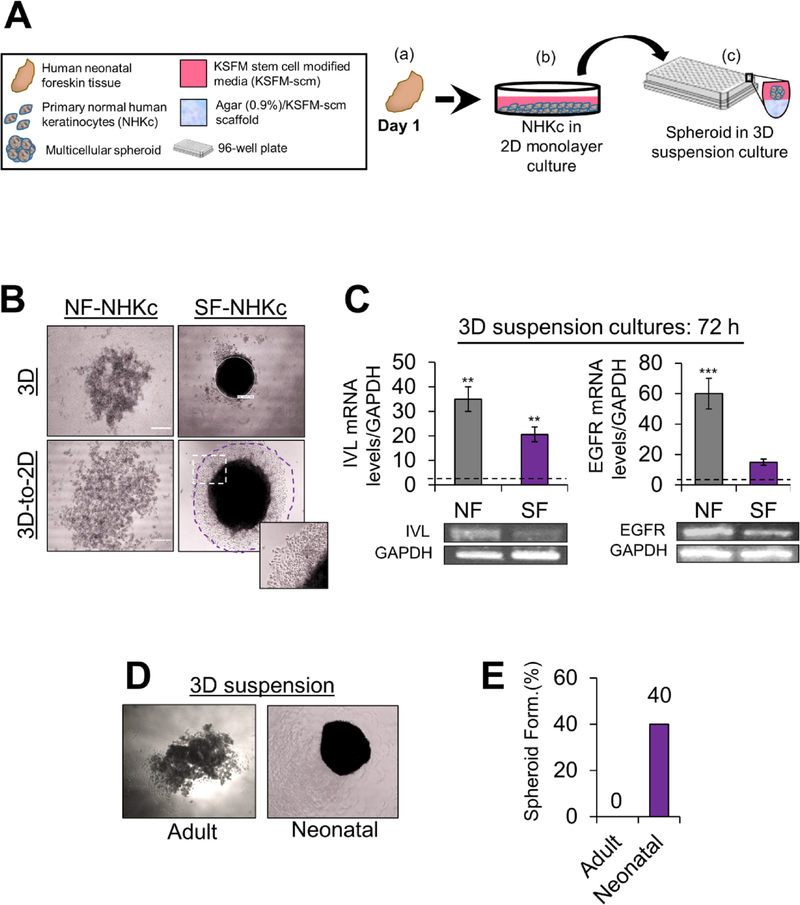
Fig. 1. Spheroid formation assay in NHKc isolates derived from different individuals.
(A) Schematic overview of the epidermal spheroid formation assay. NHKc were isolated from (a) fresh neonatal foreskin explants and (b) cultivated in 100-mm dishes, then passaged into (c) 96-well round-bottomed plates coated with a polymerized mixture of agarose and KSFM-scm. Seeded cells then generate single suspension cultures of reproducibly sized spheroids in each well. (B) 2 × 104 NHKc cultured in stem cell media were seeded onto soft agarose cushions coating individual wells of a 96-well plate. The ability for spheroid formation was assessed over the course of 144 h. Aggregation of NHKc suspensions from (left) spheroid non-forming (NF-NHKc) and (right) spheroid-forming (SF-NHKc) isolates occurred in 3-D suspension. (Bottom) 3-D cell suspensions were then transferred to 2-D monolayer culture after 48 h. Purple circle demarks propagating spheroid-derived cells captured by Nikon TMS phase microscope using Infinity 1 Analyze Software. (C) Expression levels of (Left) involucrin and (Right) EGF receptor (EGFR) mRNA, in NF-NHKc and SF-NHKc cells after 72 h in suspension culture as determined by reverse transcriptase real-time PCR relative to monolayer mass cultures. Dotted lines represent mRNA expression levels in monolayer mass cultures. (Bottom) amplicon products of each real time PCR reaction was run on a 2% agarose gel and observed by ethidium bromide staining. Data were normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels expression. Bars indicate standard deviation, and *, **, and *** indicate statistically significant P values ≤ 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001, respectively. (D) 3-D suspension cultures of NHKc isolated from (left) adult skin and (right) neonatal skin and (E) their respective spheroid forming efficiencies.