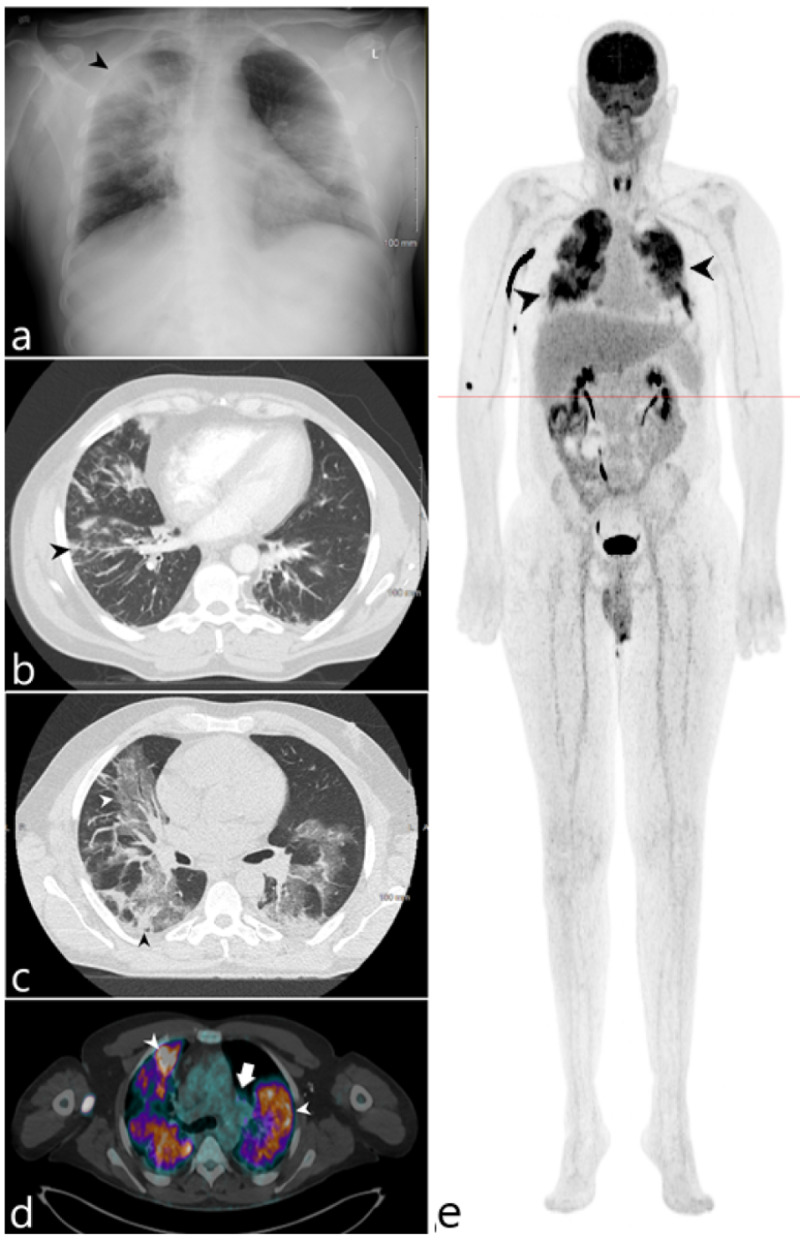
Figure 3. 54-year-old male admitted for respiratory failure in the setting of COVID-19 pneumonia.
(a) Initial admission radiograph demonstrates diffuse opacities with sites of peripheral consolidation (black arrowhead). (b) Axial CT of the lower thorax performed on hospital day 10 demonstrates multifocal peribronchovascular ground glass opacity, prominently within the right lung. (c) Axial CT of the chest acquired on hospital day 22 demonstrates worsening ground glass (white arrowhead) and consolidative opacities (black arrowhead) within both lungs. (d) Fluorine-18 FDG/PET-CT axial fused series demonstrates diffuse intense radiotracer uptake within the lungs (white arrowheads) as well as within the hilar lymph nodes (white arrow). (e) 3D maximum intensity projection image similarly demonstrates intense radiotracer uptake within the lungs (black arrowheads) without additional sites of extrathoracic radiotracer uptake.