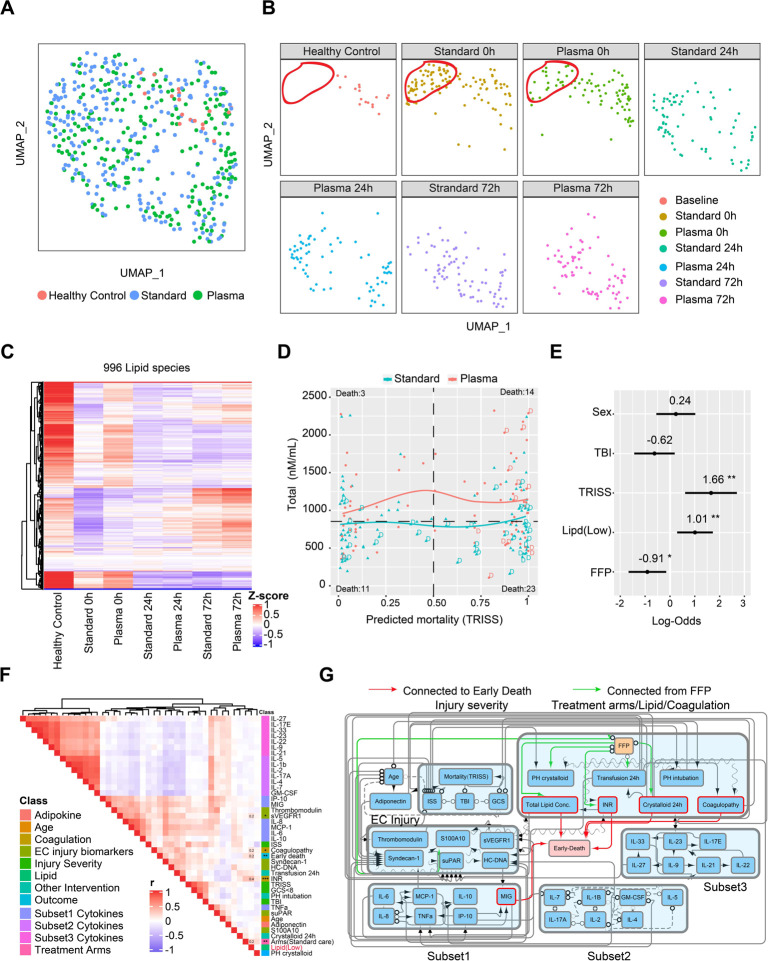
Figure 4. Potential casual effect for fresh frozen plasma (FFP), Lipid concentration and early mortality.
(A-B) Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) plot shows the distribution of healthy subjects (n=17) and patients with trauma (n=193) (A), separated by treatment arms with sampling timepoints (B).
(C) Heatmap show relative levels of 996 lipid species for healthy subjects and trauma patients, grouping by treatment arms and sampling timepoints. Exp, z-score normalized concentration. Rows are clustered by hierarchical clustering.
(D) Relationship of predicted mortality and total lipid concentration at 0h upon admission. Trauma patients are grouped by treatment arms; tendency lines are modeled by loess methods for 2 groups separately, dash line in the x-axis means 0.5 and y-axis means the median concentration. D indicates patients who died less than 72h after admission.
(E) Forest plot showing log odds ratios from logistical regression of clinical factors; Lipid concentration; FFP effect for early-nonsurvivors versus others.
(F) Correlation heatmap showing correlation among cytokines, biomarkers, clinical variables, total lipid concentration and outcome. r: Spearman correlation coefficient.
(G) Casual network among factors in (E) constructed by FCI (see also methods). The presence of “edges” or connections between nodes in the graph correspond to conditional dependencies relationships. Orientations in the causal network indicate what can be inferred about the cause-effect relationships between variables in the dataset. A directed edge A --> B indicates that A is a cause of B (i.e., a change in A is expected to affect a change in B). A bidirected edge A <-> B indicates that there is unmeasured confounder affecting both A and B. A partially directed edge A o-> B indicates that B is not a cause of A, but it is unclear whether A is a cause of B or if there is a latent confounder that causes both A and B. An undirected edge A o-o B indicates that we cannot make inferences about the causal orientation of that edge.
Abbreviations: TRISS, Trauma and injury severity score; FFP, Fresh frozen plasma; TBI, traumatic brain injury; ISS, injury severity score; GCS, Glasgow coma score; PH; Prehospital; INR, international normalized ratio.
Asterisks in (E) indicate statistical significance in multi-variable logistic regression model: *, < 0.05; **, < 0.01. Asterisks in (F) indicate statistical significance for correlation coefficient. P-values are approximated by using the t distributions: *, < 0.05; **, < 0.01; ***, <0.001.