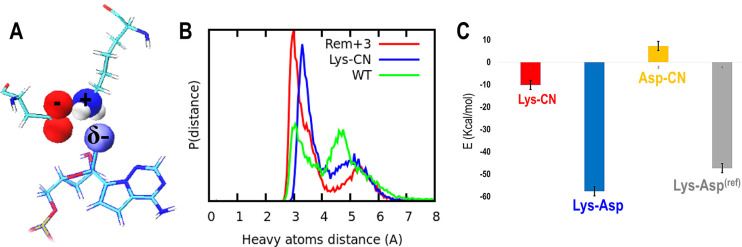
Figure 4.
(A) Protein–remdesivir interactions when this non-natural nucleotide is located at position i+3: aspartic acid, lysine, and remdesivir are shown with sticks. Atoms belonging to the carboxylate functional group, cyano, and amino are highlighted with spheres (van der Waals radius), where red represents oxygen atoms, blue for nitrogen, and white for hydrogen. (B) Probability distribution distances for salt bridge and hydrogen bond interactions between lysine and aspartic acid when remdesivir is located at the i+3 position (blue), lysine and aspartic acid for the wild type system, without remdesivir (green), and hydrogen bond among the remdesivir cyano group and lysine (red). C) Bar chart: in red the total summary of pairwise interactions for the lysine and remdesivir cyano functional group, in blue the lysine and aspartic acid salt bridge when remdesivir is located at position i+3, in gray the lysine and aspartic salt bridge for the wild type (WT) RNA, and in yellow the repulsive contribution for interactions among the aspartic acid and cyano functional group belonging to the non-natural nucleotide, remdesivir.