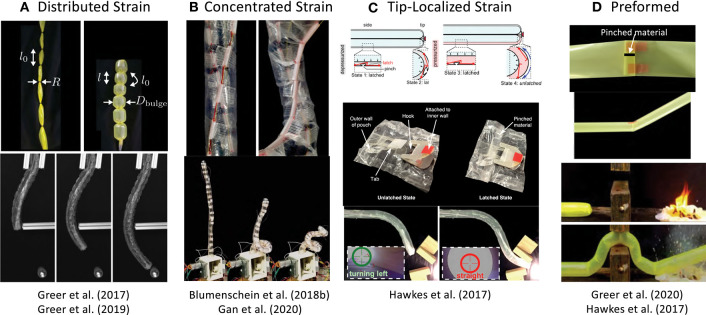
Figure 3.
Methods of actuating everting vine robot growth direction and shape, including (top) actuation principles and (bottom) examples of implementation. (A) Distributed strain uses pneumatic artificial muscles to create strain along the length where they are attached. (B) Concentrated strain uses tendons actuated from the base to change the robot shape. (C) Tip-localized strain couples steering and growth to create responsive steering at the tip only. (D) Preformed steering shapes the robot for known tasks before deployment. Modified from Greer et al. (2019). The publisher for this copyrighted material is Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. publishers. Modified from Greer et al. (2017) © IEEE 2017, Blumenschein et al. (2018b) © IEEE 2018, and Gan et al. (2020) © IEEE 2020. Modified from Hawkes et al. (2017). Reprinted with permission from AAAS. Modified from Greer et al. (2020).