Figure 6.
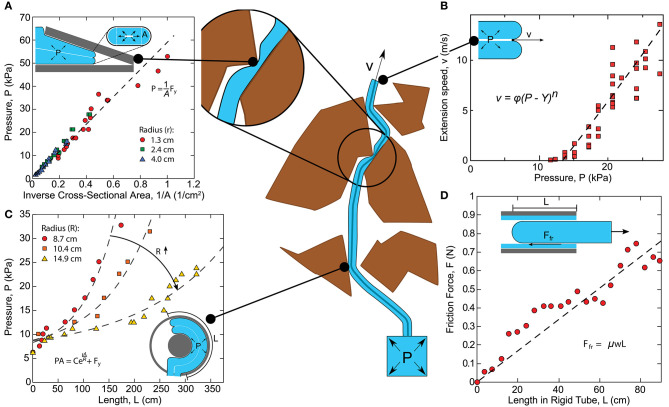
Quasi-static modeling of everting vine robot growth. Model relates the driving force (internal pressure times tip cross-sectional area) to the losses due to the robot state, including (A) static yield force (i.e., driving force required to begin growth), (B) viscoplastic loss due to everting material, (C) exponential friction for moving tail material around curves in path, and (D) linear friction as a function of length/weight of tail material being transported. Modified from Blumenschein et al. (2017). Reprinted with permission from Springer Nature.