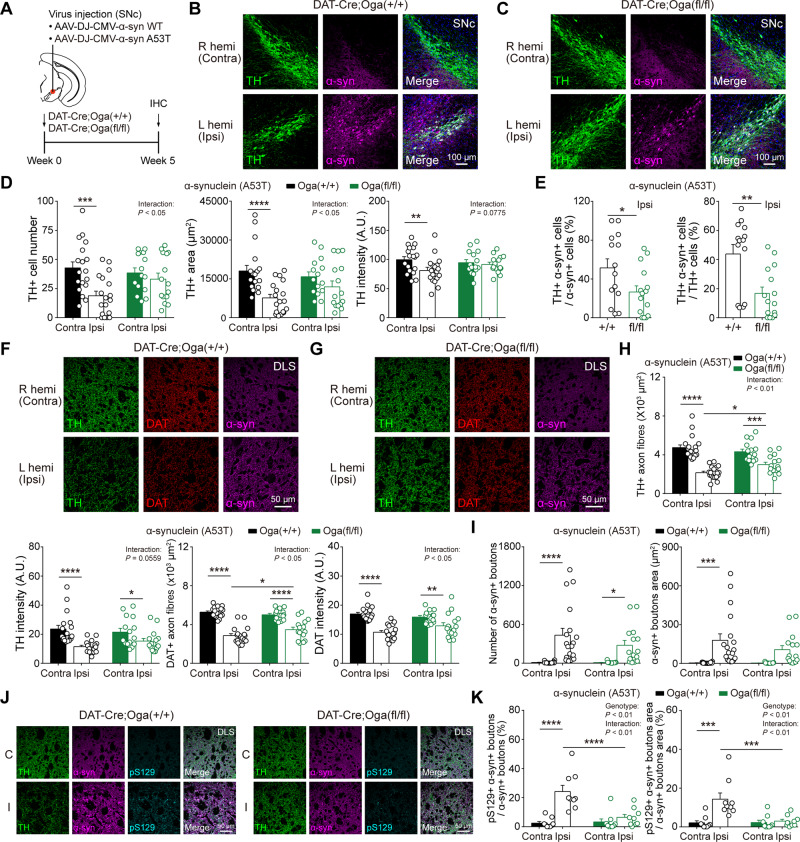
Figure 6.
α-Synuclein-induced neurodegeneration is alleviated by upregulation of O-GlcNAcylation. (A) Schematic illustration describing the injection of α-synuclein AAV viruses [wild-type (WT) and A53T] into SNc (left hemisphere). (B and C) Representative confocal images of TH and α-synuclein immunofluorescence from SNc dopamine neurons in DAT-Cre;Oga+/+ and DAT-Cre;Ogafl/fl mice injected with A53T virus. (D) Quantification and summary statistics of TH immunoreactivity in SNc. (E) Co-localization of TH and α-synuclein in ipsilateral SNc. (F and G) Representative confocal images of TH, DAT, and α-synuclein immunofluorescence from DLS in DAT-Cre;Oga+/+ and DAT-Cre;Ogafl/fl mice injected with A53T virus. (H) Summary statistics of TH and DAT immunoreactivities in DLS. (I) The number and area of putative α-synuclein+ synaptic boutons in DLS. (J) Representative confocal images of TH, α-synuclein, and pS129 immunofluorescence from DLS in DAT-Cre;Oga+/+ and DAT-Cre;Ogafl/fl mice injected with A53T virus. C = contralateral; I = ipsilateral. (K) Co-localization of α-synuclein and pS129 in DLS. Data were analysed by repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s post hoc test (D, H, I and K) and unpaired t-test (E). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.